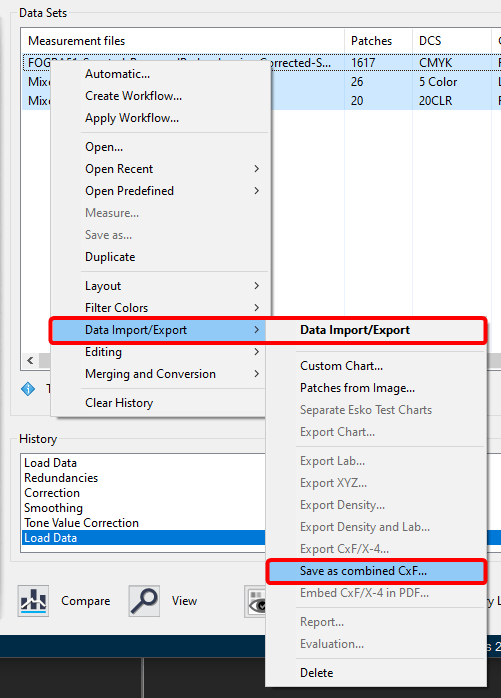
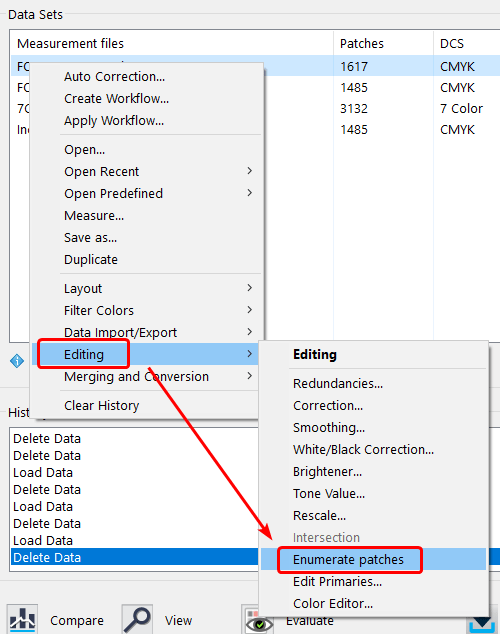
ColorAnt | Report
Create Report
Overview
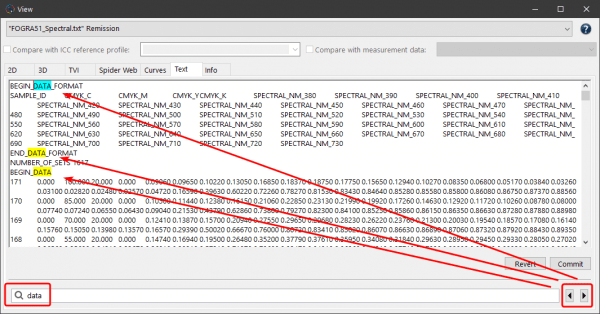
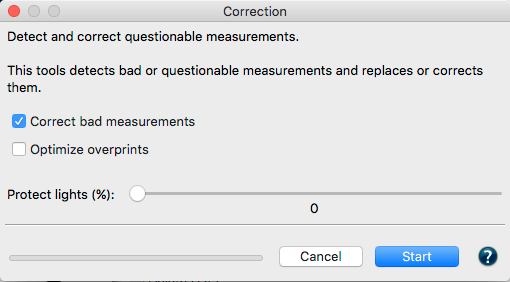
If there are questions about the quality of the measurement data for further processing (e.g. for creating profiles) or if measurement data needs to be corrected, you can create a Report. This report is used to verify and graphically display the data and to provide recommendations for corrections. The Report is a very powerful feature to indicate the necessary corrections to the measurement data and provides useful comparisons.

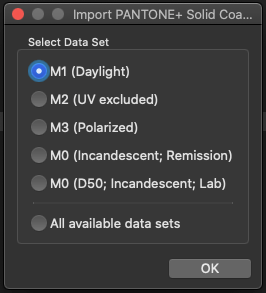
Note: The Report tool is available, when a single data set or multiple data sets of the same color space are selected.
Multiple reports can be generated at once for several selected measurement data. In this case, individual reports for each of the selected data sets will be generated.
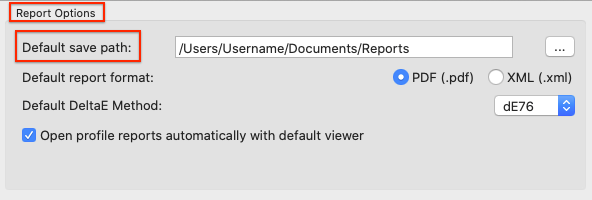
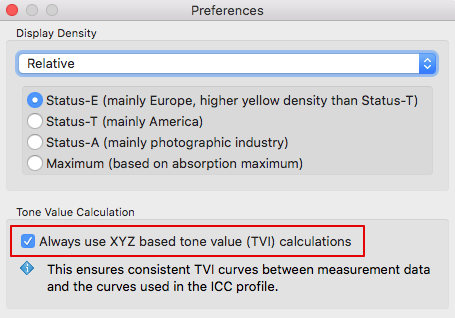
Under Preferences, the Default save path for the reports and the Default report format can be selected. If XML is selected as the format, the corresponding XSD files will be created automatically as well.

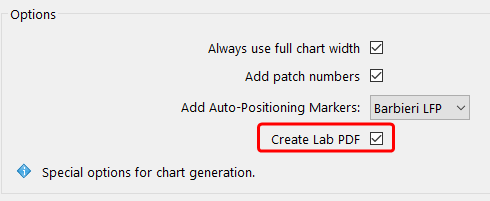
Specifics of the PDF Report
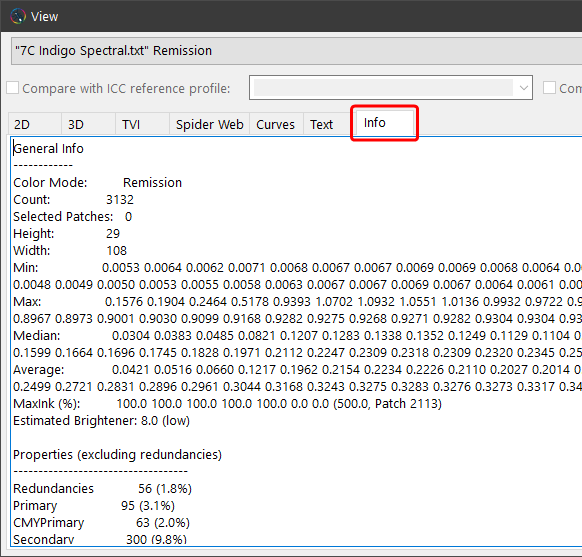
The different reports provide an insight into measurement or printing errors and the smoothness of the measurement file. Text assessments in the individual sections give tips on the correction tools to be used in ColorAnt. Get information about optical brighteners in the paper, which available ICC profiles best fit the measurement data, or how exactly the measurement data depicts a pre-defined reference profile.
The Brightener section gives some useful information about the detected OBA in the file, for example the Estimated Brightener and how a brightener correction would affect the paper white. This is based on a predictive model that focuses exclusively on the change of the b* value, which is used as an indicator for the brightener share in the paper.
However, the actual correction could affect all L*, a*, b* values and result in a slightly different value (dE) than the predictive brightener indicator shows.
Delta b*: OBA share in paper
Delta b* < 1 = faint OBA
Delta b* < 4 = little OBA
Delta b* < 8 = low OBA
Delta b* < 14 = moderate OBA
Delta b* > 14 = high OBA

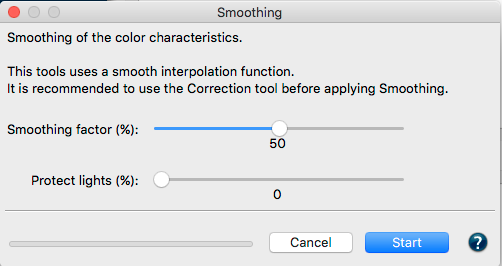
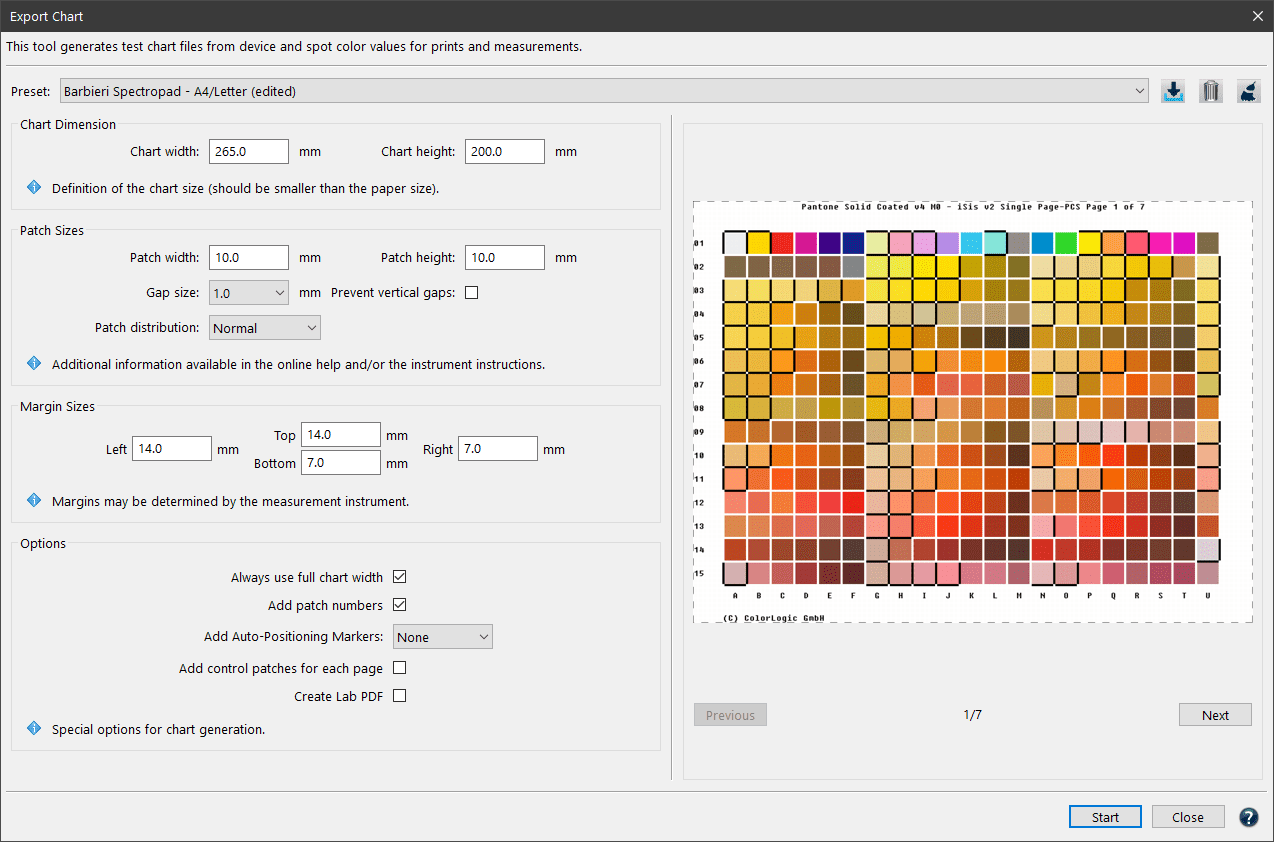
Display the required tone curves by switching on/off the different layers in the PDF file. Switch on/off the color patches highlighted with a red frame and also view color patches before and after correction and smoothing.
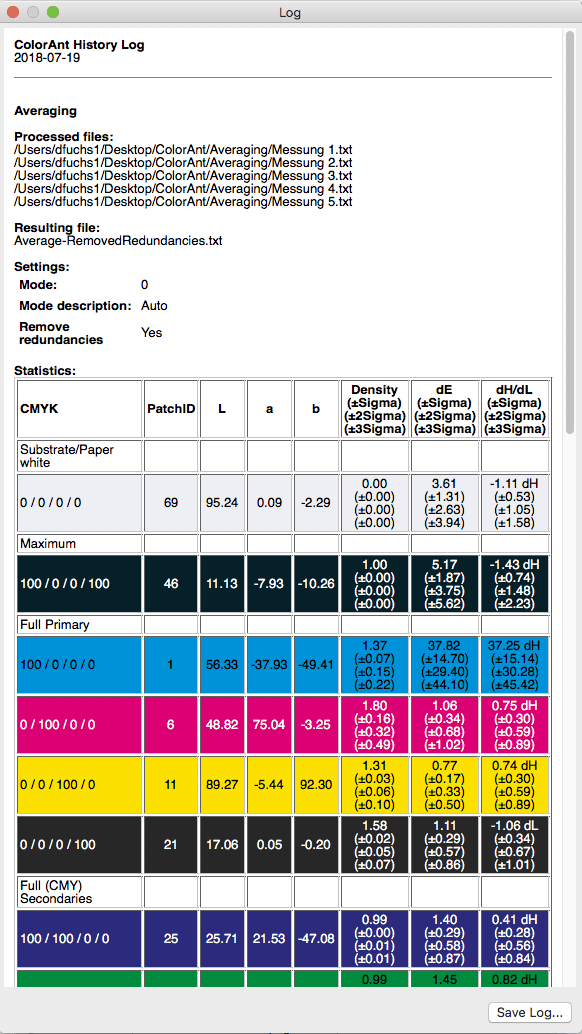
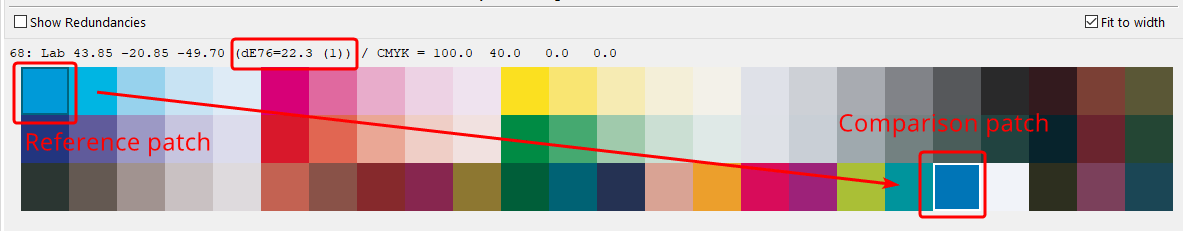
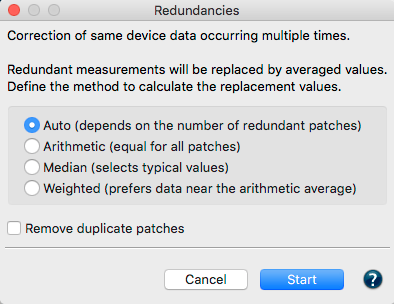
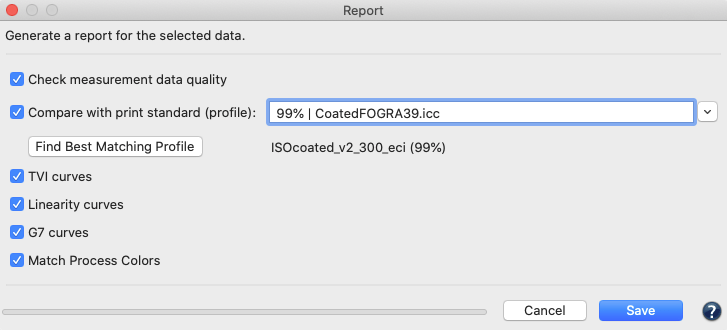
Check measurement data quality: Examines the measurement data and lists the results in the report, e.g. whether redundancies exist. The report also shows how much the application of data optimizing tools, such as correction and smoothing, would affect the data.
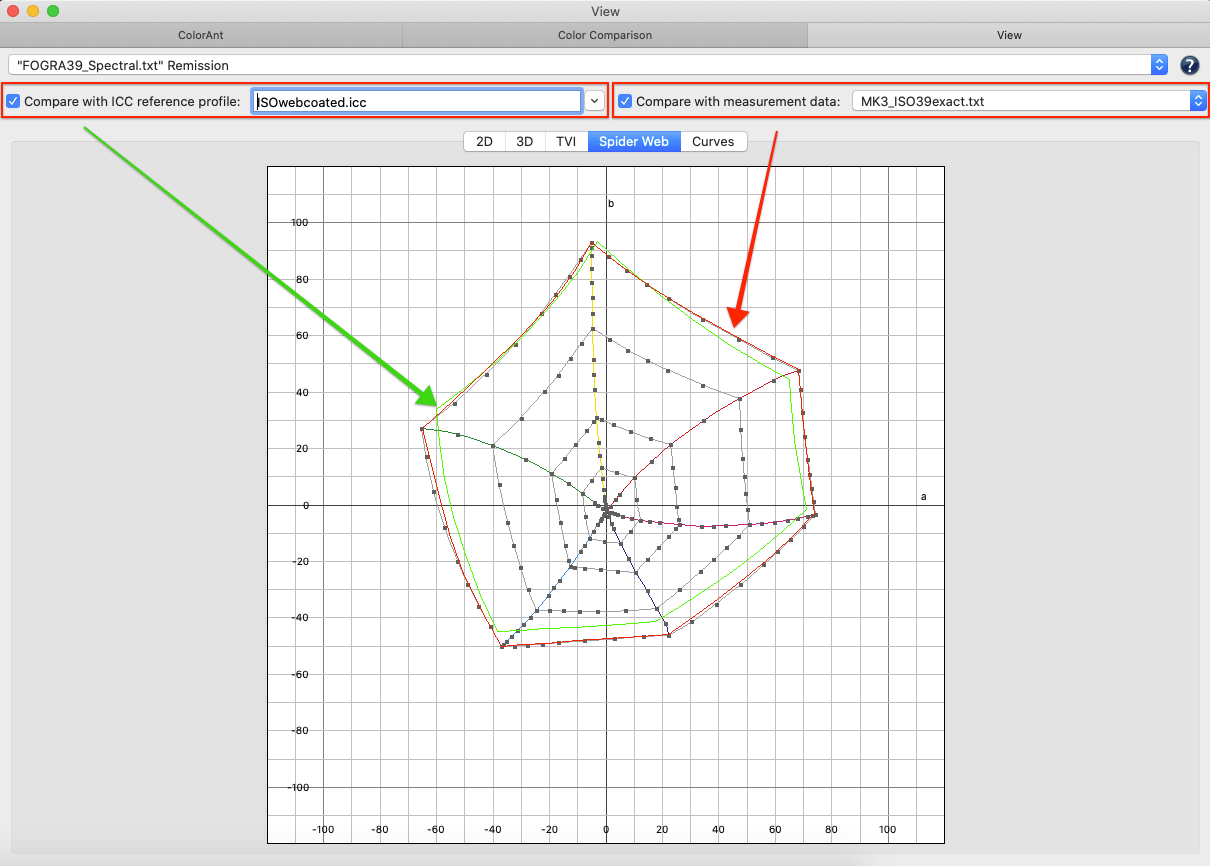
Compare with print standard (profile): Compares the measurement data with the selected reference profile and indicates the accuracy of color matches. Activate this checkbox to select a comparison profile. ICC profiles in the drop-down menu are shown with the matching percentage in front of the profile name and are sorted by percentages with the highest match on top. The best matching profile of the list will automatically be selected if the Find Best Matching Profile button is clicked.
Find Best Matching Profile: Automatically selects the best matching profile for comparison with the measurement data. Enabled for a single data set, disabled for multiple data sets.
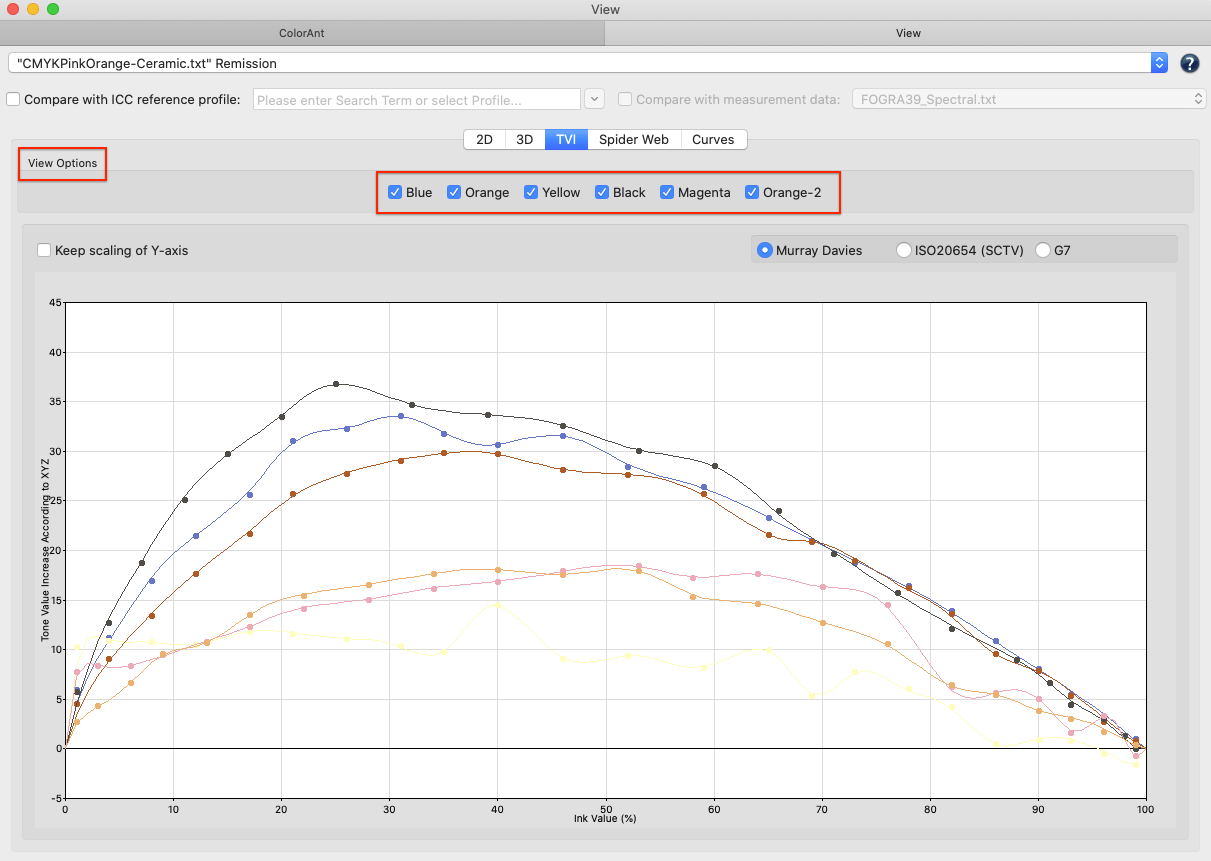
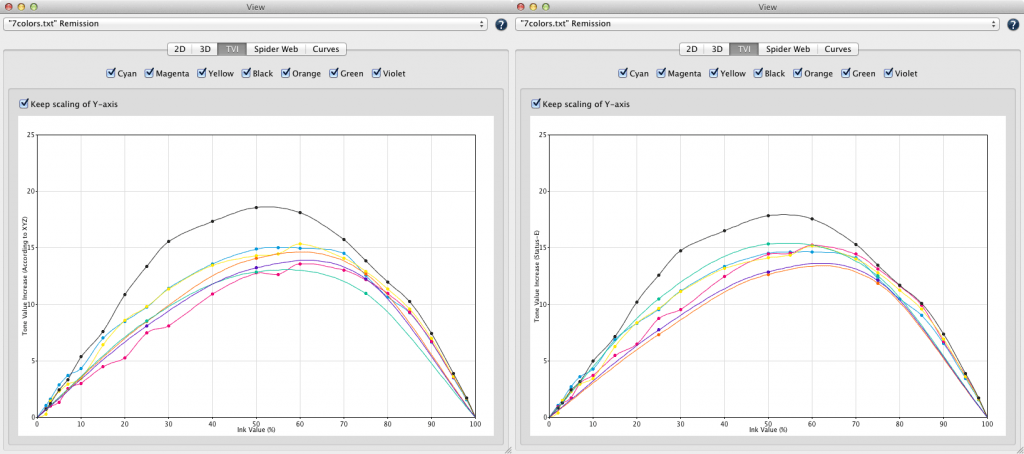
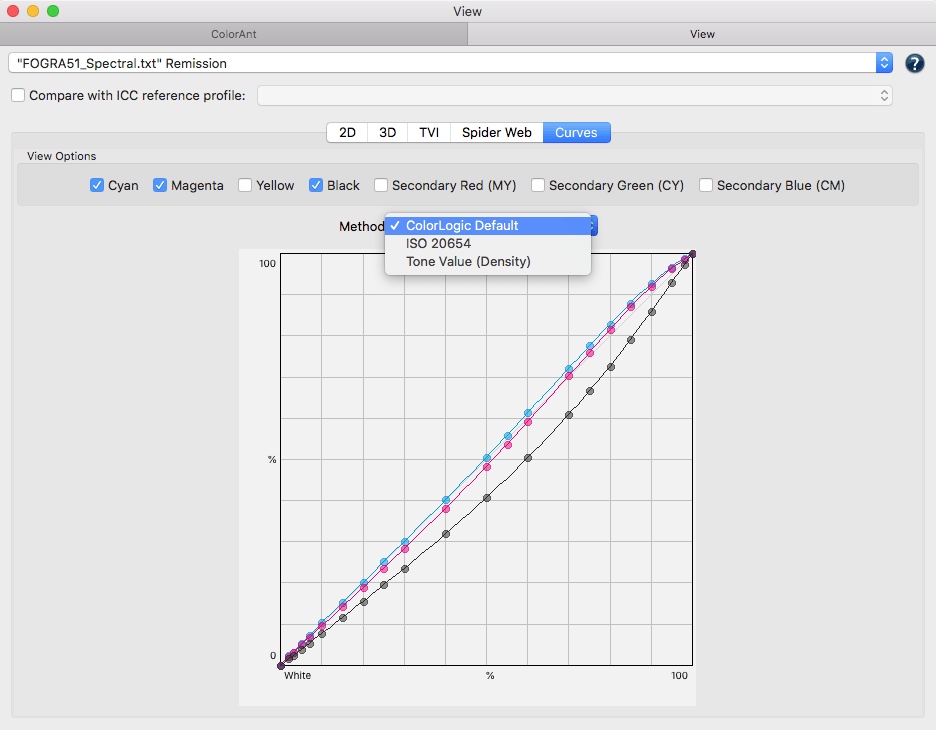
Include TVI curves: Includes the tone value increase curves in the report.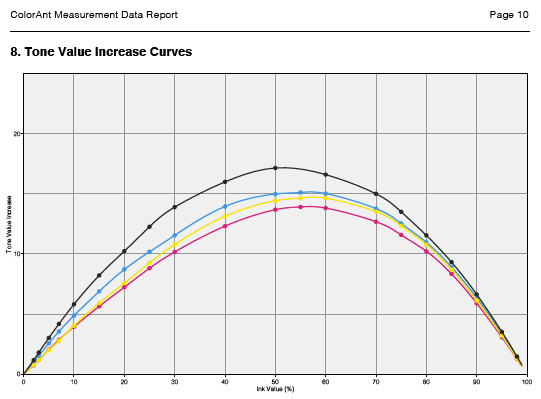
Include linearity curves: Shows the linearity curves in the report.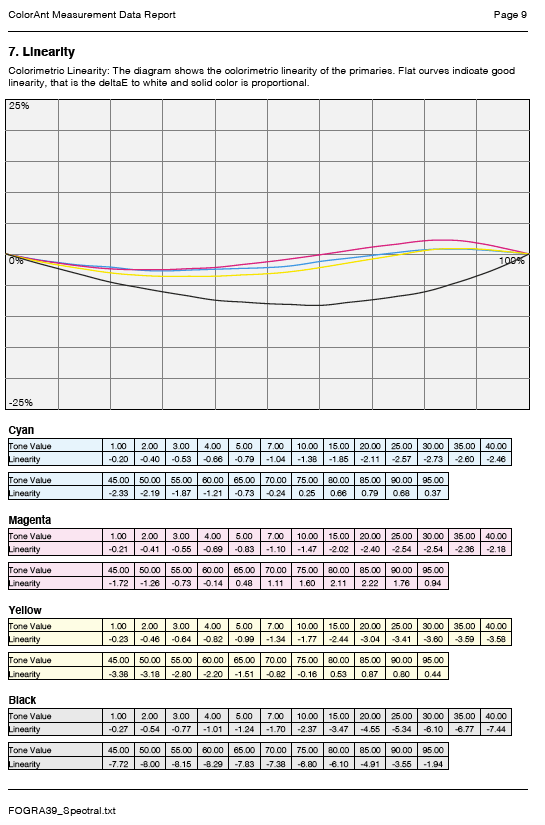
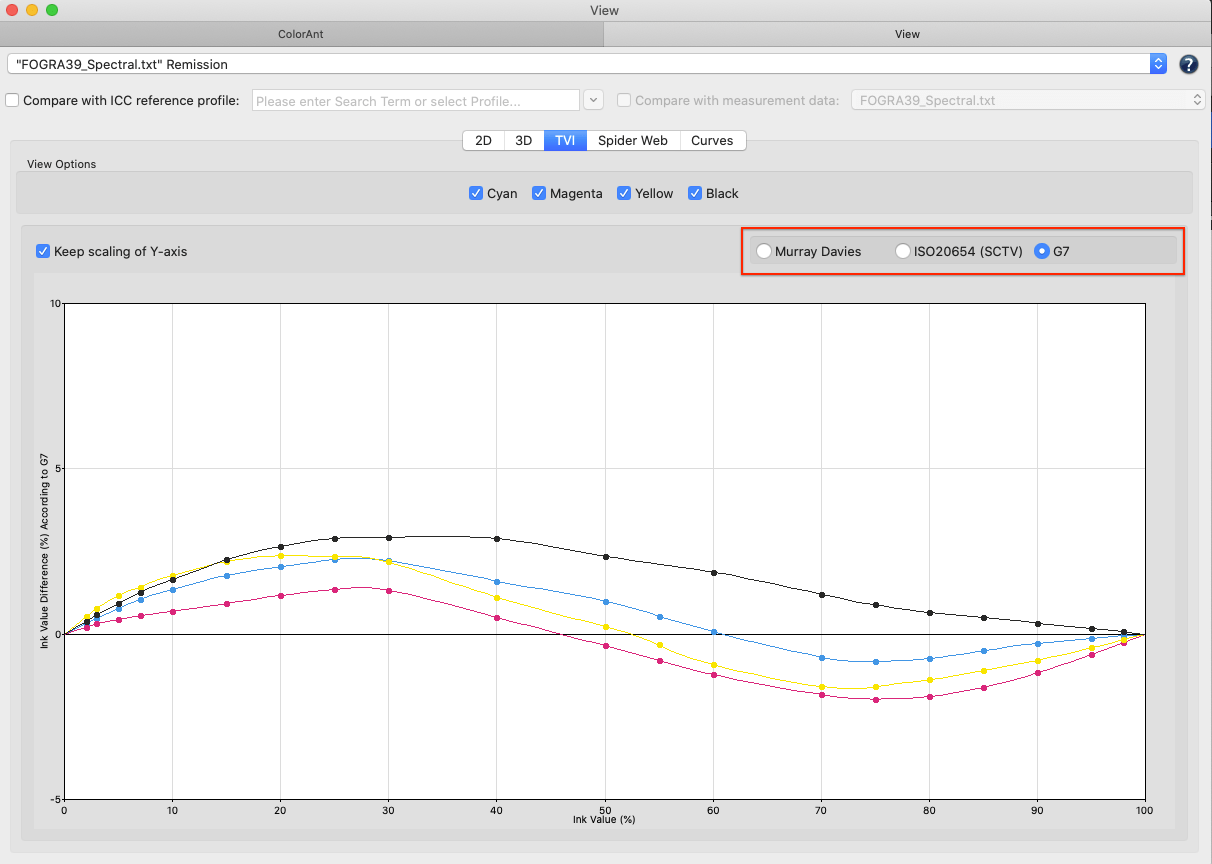
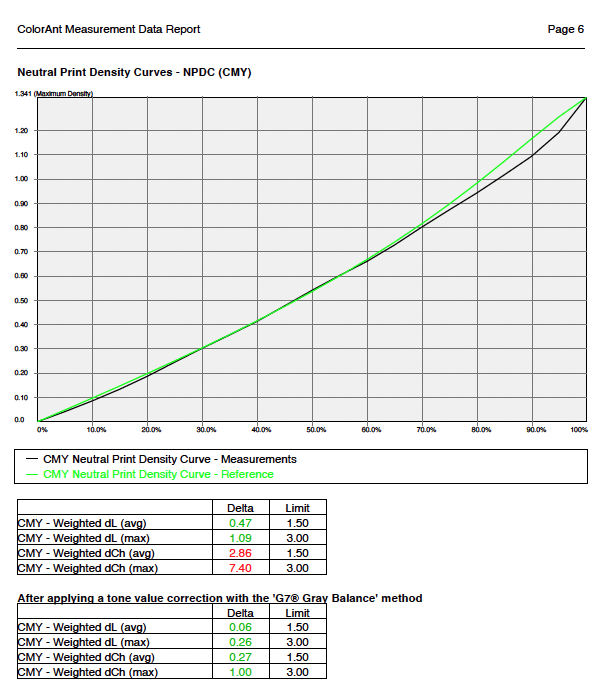
Include G7 curves: If activated, the selected CMYK or CMYK + data is checked for G7® compliance. The Report shows three graphs. The first graph indicates the Tonality / Gray balance according to G7 curves in relation to the G7® aim. Flat curves indicate a perfect G7® gray balance. The two other graphs show the Neutral Print Density Curves (NPDC) for CMY and K. In these graphs Reference (green curve) represents the desired target curve for G7® conformity and Measurements (black curve) represents the curve of the measured values. A perfect G7® match shows identical curves for the measurement data and the reference.
Note: G7® is defined for CMYK only. For Multicolor data only the CMYK parts are analyzed.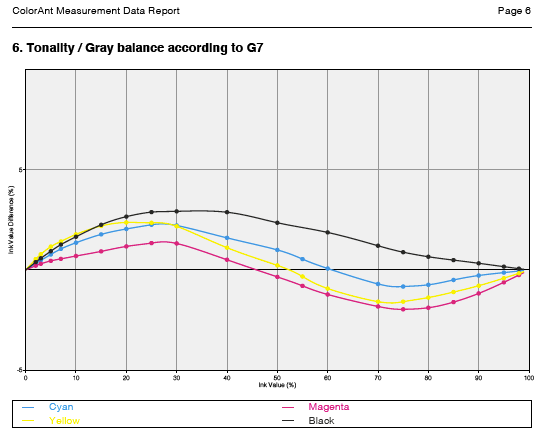
When Include G7 curves is activated, the report shows the various NPDC curves before and after the calculation and the G7® evaluation based on the measurement and calculation data.
The Weighted avg/max before (Measurements) and after (After applying a tone value correction with the ‘G7® Gray Balance’ method) are shown in tables for CMY and K respectively. This makes it easy to check whether a limit has been exceeded (red values) or not (green values).
Match Process Color: Activate this checkbox to determine whether a close match between the measured solid process colors and the reference solid process colors (defined by the selected profile) can be achieved by adjusting the density or percentage values. Only the solid process colors of the loaded data set are used and compared to the selected profile. Therefore, this feature is only enabled if a comparison profile (Compare with print standard) has been selected.
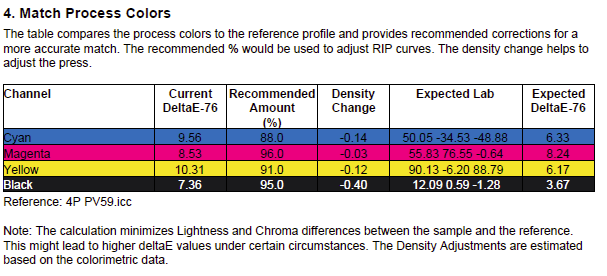
Functional principle
- Finds closest possible match to the reference based on recommended densitometric and percentage adjustments
- Gives adjustment recommendations to increase or decrease density
- Recommends Process Color % values to be entered into a RIP curve to match the reference primaries
- Shows original DeltaE values and expected DeltaE values after the recommended optimization
- Provides a quick and easy interpretation for printers and press personal if a match is possible and how to achieve it
The calculations minimize Lightness and Chroma differences between the sample and the reference for CMYK and Multicolor primaries. The density recommendations are an estimation based on colorimetric densities. The DeltaE values provided are either dE76 or dE00 depending on the setting under Preferences. Note that the expected DeltaEs may be higher than the initial values. This indicates that a perfect match is not possible.
Save: Reports are saved automatically in the folder defined under Preferences/Report Options/Default save path. Make sure that you have specified the preferred report format, the DeltaE method to be used and whether the created report(s) should automatically open in the default PDF viewer (under Preferences/Report Options). The report file automatically receives the file name of the selected data set including the creation time.