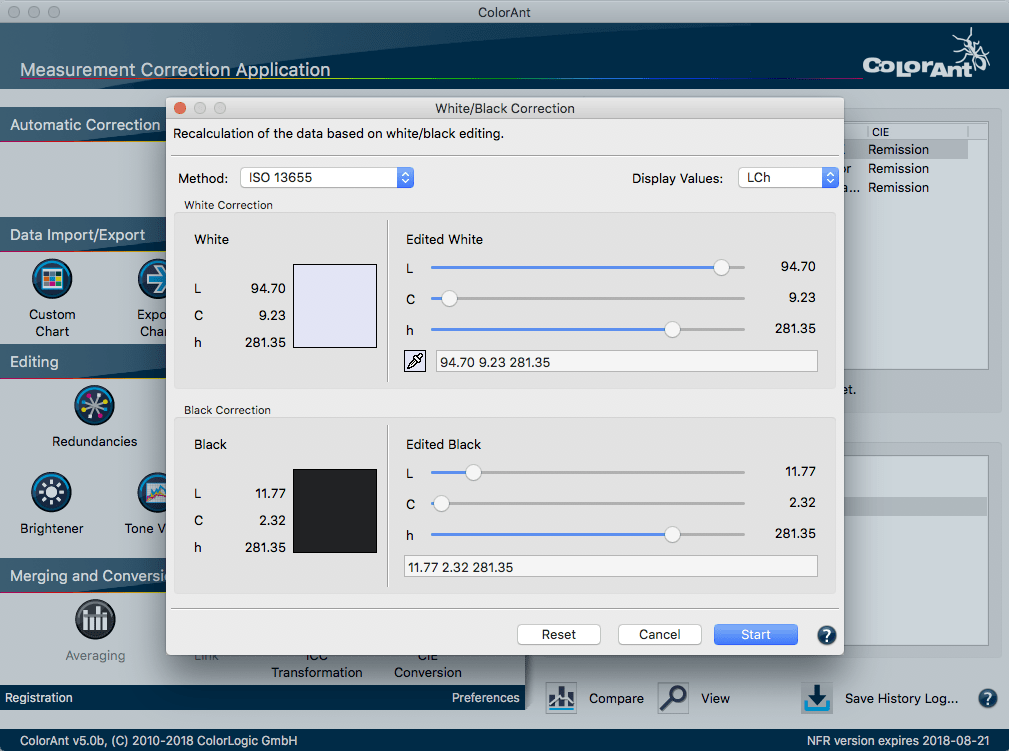
Correcting the White and Black Point
Overview
This tool allows adjusting the paper white using the White Correction and the darkest color using the Black Correction.
The White Correction tool allows manual correction of the whitest patch of the measurement data, which is usually the paper or substrate color. The tool is applied to a single measurement file. A correction by changing the Lab or LCh input value is useful in cases where either a specific target white point is to be achieved or corrections are required to lighten, darken or recolor the data. The manual correction is then applied to the entire measurement data, leaving the print characteristics intact.
White Correction: This calculates the effect of the changed paper white on the measurement values of a test chart. In ColorAnt, three different methods are available for calculating this effect: ColorLogic Default, ISO 13655 and Relative colorimetric.
Direct Measurement of the White Point
Changes in paper white affect the entire color space. Major changes in paper white also have a strong effect on the primary colors.
The white point can be (re-)measured directly from within the White/Black Correction tool. This measurement data can then be used to correct the white point of the selected dataset.
Follow these steps to adjust the white point:
- Load the measurement data to be corrected and open the White/Black Correction tool.
- Click on the eyedropper icon and select the option Measure.
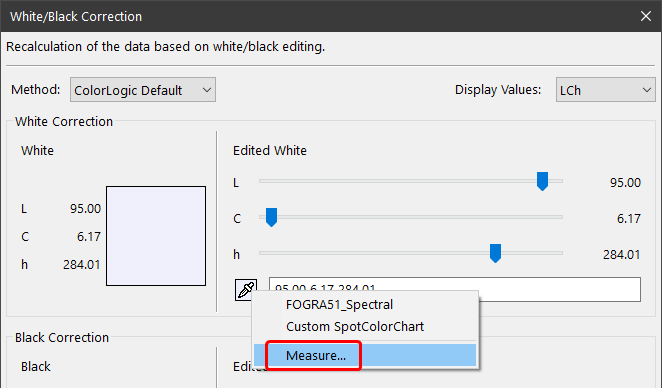
- The Measure Tool opens with the preselected chart for measuring the paper white with a single patch.
- After the measurement, the new white point data is transmitted back to the White/Black Correction tool and is applied to the entire measurement data keeping the print characteristic intact.
Note: The white point measurement is also listed under Data Sets.
White Correction Methods
ColorLogic Default: This method uses a spectral color model to apply corrections that produce the most realistic results possible. This works best when both the data to be changed and the white taken from another file are spectral data. If spectral data is not available, ColorLogic Default works in the same way as ISO 13655, assuming that shadows are not affected and that the impact on primary colors is much smaller.
ISO 13655: In the highlight areas and colorful primary colors, this method is similar to the Relative colorimetric method. However, this method assumes that the shadows and very dark colors are not changed.
Relative colorimetric: Changing the paper white will modify the entire color space. Major changes to the paper white also have a strong effect on the primary colors.
Procedure for White Correction:
- Load the measurement data to be corrected and the data containing measurements of the new paper white.
- Click on White/Black Correction
- Select the mode for adjusting the corrections: LCh or Lab Color Mode. The mode can be changed at any time. With LCh the hue or chroma can be adjusted independently, while the corrections in a* and b* change hue and chroma simultaneously. The split color patch displays the original white on the left side and the modified white on the right side.
- The white point can be edited either manually with the sliders or by entering Lab values. Alternatively, a new white point can be selected from another data file using the eyedropper icon. Simply click on it and select the data file that contains the desired white point. The new white point will be selected automatically.
Notes: The eyedropper will pick the whites patch of the selected file. If spectral data is detected, the tool will use it according to the selected Method.
The sliders allow for small changes. More precise numbers can be entered in the dialog box. The sliders are reset afterwards. - If the lightness (L* value) is changed while using the Relative colorimetric method, the darkest colors of the measurement files are usually affected as well. If the black point and the darkest colors are not to be changed, the ISO 13655 method should be used. Both methods, Relative colorimetric and ISO 13655, apply calculations with colorimetric data. Only the ColorLogic Default method uses the full spectral data and a spectral model for the calculation.
Note: Depending on the color difference of the paper white and the presence of optical brighteners, this may affect the primary colors. - Clicking the Reset button will discard any slider modifications.
- Clicking the Start button applies all changes to the entire measurement file. The dialog is closed automatically after the calculation.
Black Correction
Black Correction: This method can be used to change the darkest black, thereby scaling the entire dataset to the modified black point. This is beneficial when black has been measured too dark or too light compared to the visual appearance. Common scenarios include materials used in industrial applications such as ceramics, textiles, glass, etc.
Important: Black Correction is not available when using the Relative Colorimetric Method.
Procedure for Black Correction:
- Load measurement data.
- Click on White/Black Correction.
- Select either ColorLogic Default or ISO 13655.
Note: Relative colorimetric does not allow changes to the black point. - Adjust the correction in LCh or Lab Color Mode. LCh allows adjustment of the hue or chroma independently whereas corrections in a* and b* will change hue and chroma simultaneously. The split color patch displays the original black on the left side and the modified black on the right side.
- The black point can be edited either manually with the sliders or by entering Lab values.
- Click the Reset button to discard any slider modifications.
- Click Start to apply the corrections. The dialog is closed automatically after the calculation.

