ColorAnt | Export Chart
Export Chart
Overview
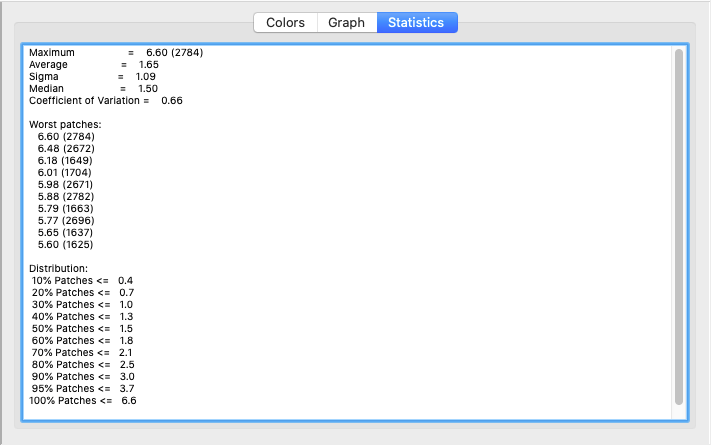
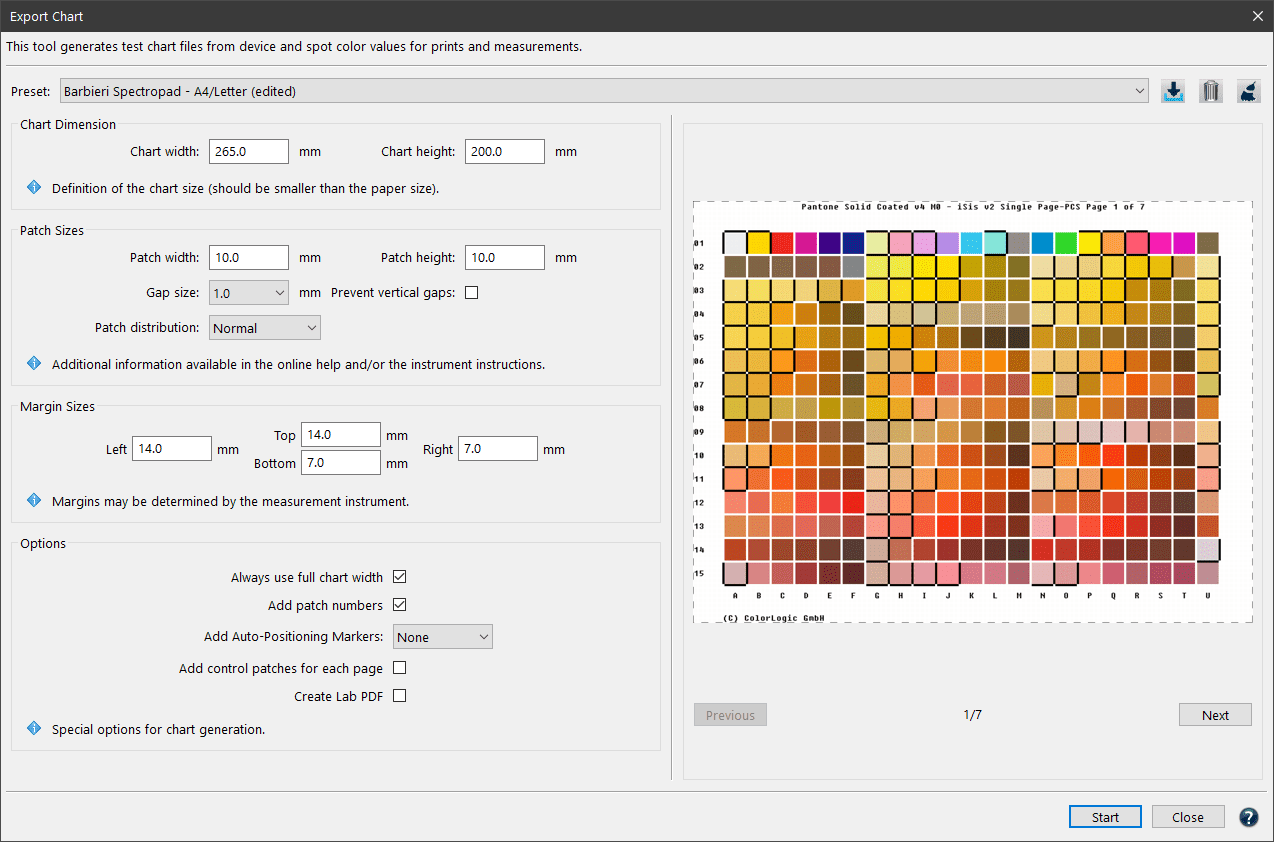
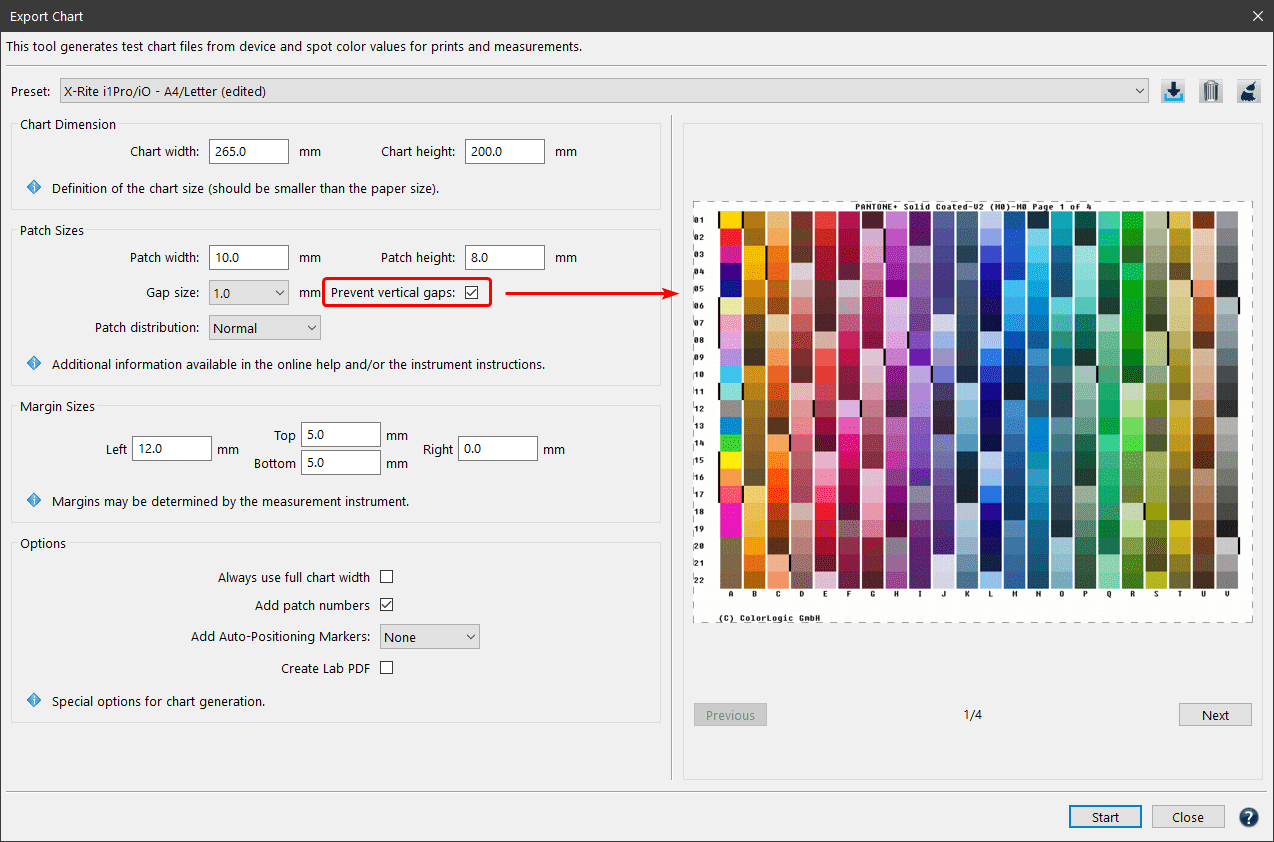
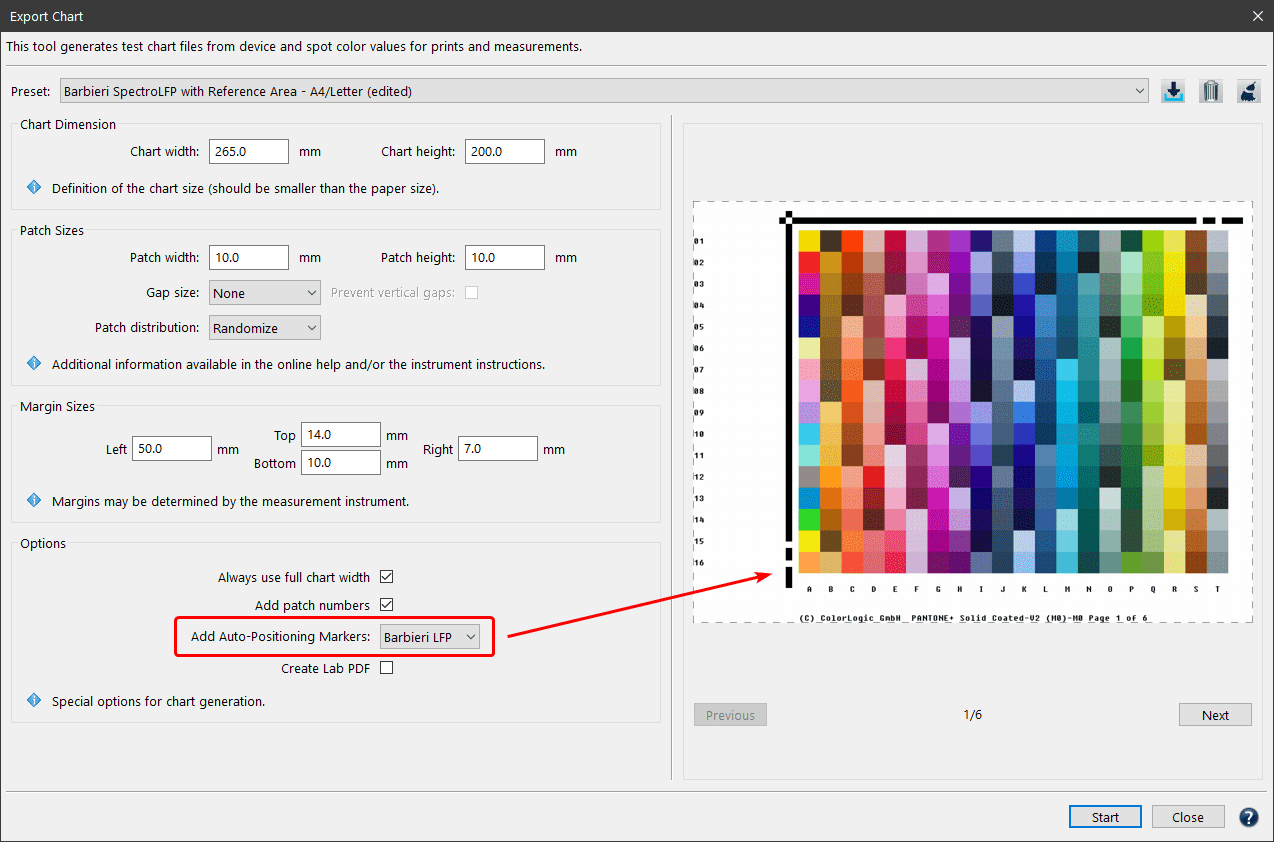
The preview area on the right side shows the Patch distribution on all generated pages. Changes of the Chart Dimension, Patch Sizes and Options can thus be evaluated directly.
On the bottom of the window are buttons to Cancel or create (Start) the test charts.
The Measure Tool is optimized to work with most instruments:
- Barbieri Spectro LFP
- Barbieri Spectro LFP qb
- Barbieri Spectropad
- Konica-Minolta FD-5
- Konica-Minolta FD-7
- Konica-Minolta FD-9
- MYIRO-1
- MYIRO-9
- Techkon SpectroDens (Windows only)
- Techkon SpectroJet (Windows only)
- X-Rite eXact
- X-Rite eXact2
- X-Rite i1Pro 1
- X-Rite i1Pro 2
- X-Rite i1Pro 3
- X-Rite i1iO
- X-Rite iO3
- X-Rite i1iSis 2/XL
Note: Non-supported instruments may require software from the specific vendor for generating a test chart from our reference data. Read this article about using ColorLogic reference data in other programs such as X-Rite i1Profiler to generate test charts for the X-Rite iSis.
Procedure
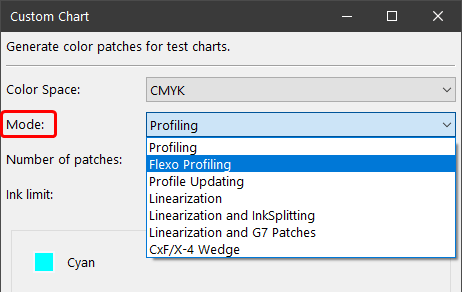
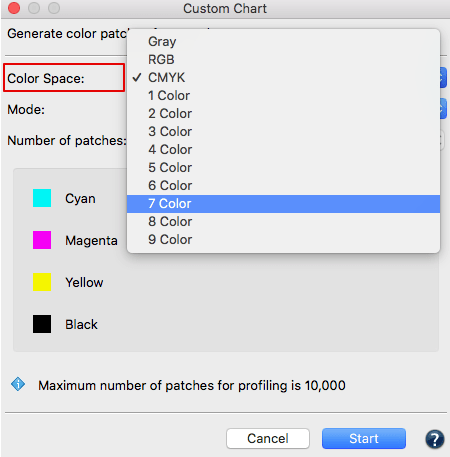
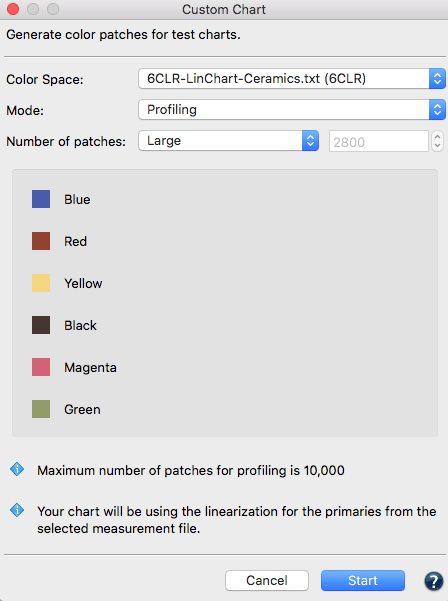
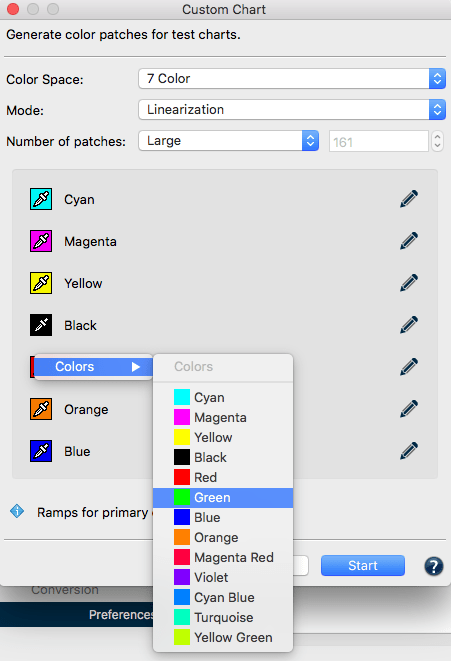
- Select the reference file with the required device color values and load this information into Measurement Data. Available reference data for different color spaces are stored under Data/ Predefined data or create your own reference data with the Custom Chart tool.
- Open the tool Export Chart to define the proper settings for creating a test chart for the applicable measurement device.
- It is recommended to select a Predefined Preset in the drop-down menu that fits your instrument type and size requirements.
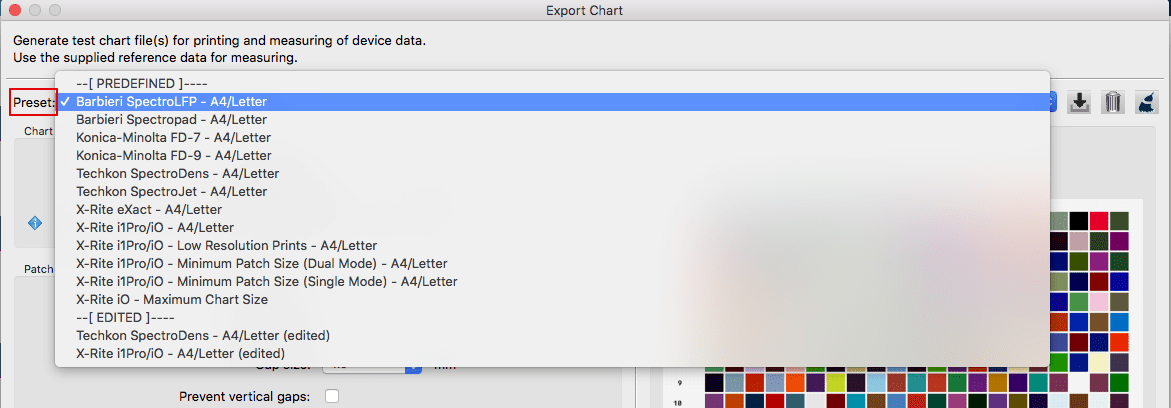
The Broom icon can be used to delete edited presets if they haven’t been saved yet.
- For a custom chart or patch size edit one of the predefined presets. The edited version will be marked as (edited). For the custom settings to be saved click the save icon and give the preset a name. Saved presets will be listed under the SAVED divider line in the drop-down menu.
- After defining the settings (more details in the next chapter Settings and Options) ColorAnt will display how many pages the test chart will require. A larger Chart height allows more patches per page and reduces the number of pages required.
- Click on the Start button and the test chart will be exported. In the Save dialog define file name and Format (TIFF, PSD or PDF).
- ColorAnt generates the required test charts and the corresponding reference data that match the specified layout. Please use this newly generated reference data and not the one loaded under point 1 for measuring the patches and profile creation.
Note: ColorAnt can create reference files from PDFs that contain spot colors. This implies that files containing NoSpace/Lab information can also be exported (see below for more information).
Settings and Options
Measuring instruments may have specific needs regarding patch sizes, the gap between different patches and the size of the overall chart. In addition, you may respect the requirements of your print process and eventually reduce the Ink Limit (TAC).
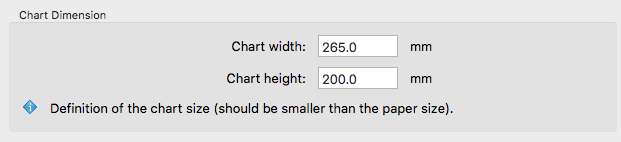
Chart Dimension
Define the image size of each individual test chart. Enter the desired Chart width and height to limit the space that might be used for the color patches (minus the space required for labeling the patches). This is the image size, not the paper size. The exported test charts can be positioned on the required paper size afterward and then be printed.
Patch Sizes
Allows you to define the Patch width and Patch height of each color patch. Select the Gap size from the drop-down menu. Use Auto as a default or None if no gaps between patches are needed. Some instruments can work with a very small gap of 0.5 mm some require 1 mm. For rough surface substrates and low resolution printers a 2 mm gap may be helpful. For further information consult the instrument documentation.
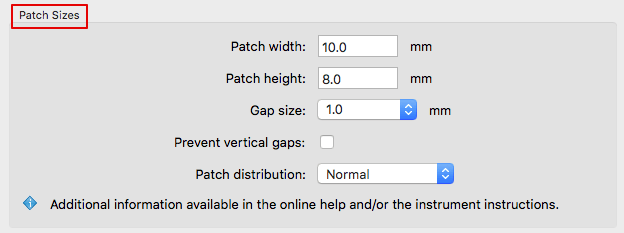
Prevent vertical gaps: Removes the gaps between rows (gaps between columns remain). Depending on the chart size, several additional rows may fit on one page.
Patch distribution: Defines the distribution of patches on the test chart.
Randomize: Color patches are distributed randomly.
Normal: Color patches are distributed as specified in the reference file.
Sorted: Color patches are sorted from light to dark. This might be helpful to modify a random chart into a well sorted layout or if you export a color wedge of one single color.
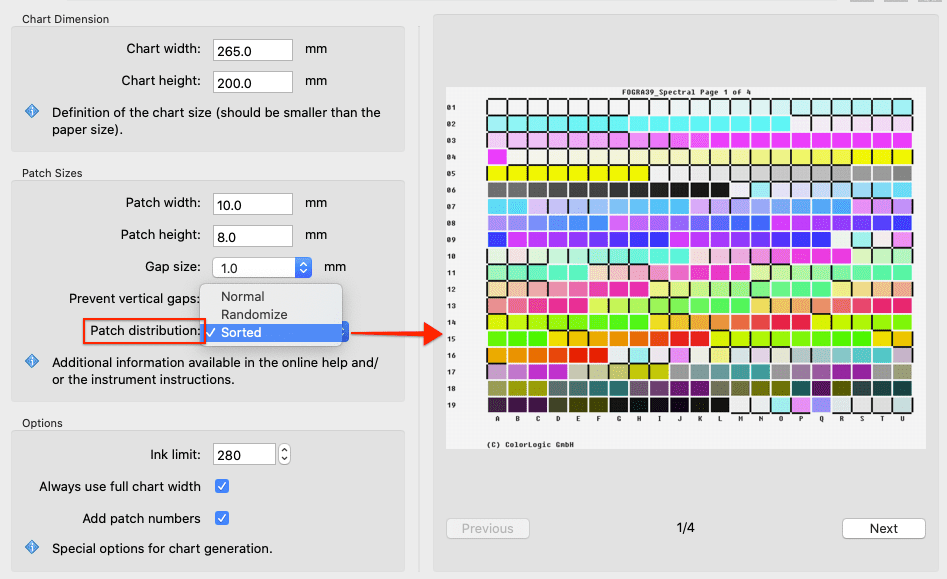
Note: Randomize is applied every time you save the file. So it is not possible to save the same reference file with the same random patch order twice. If it is however wanted, we recommend the following workaround: Save your chart with Randomize and open the generated reference to save it again using a Normal patch distribution.
Chart defining data such as chart size, Rows per page and Gap Size are stored in the reference file. When measuring the test chart using the Measure Tool, all supported measuring devices that have Setup Wizards (for example the i1iO, Konica-Minolta FD-9 and the Barbieri devices) read out this data and automatically import it.
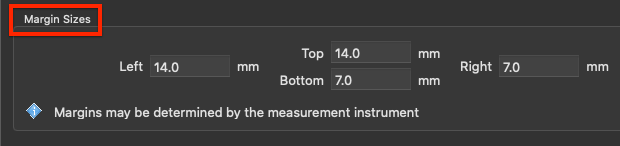
Margin Sizes
This section enables user-defined margins for test charts. This is important for measurement devices that require an additional “white-space” before and after lines to be measured.
Options
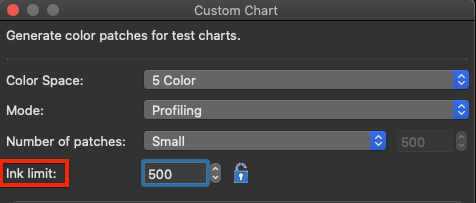
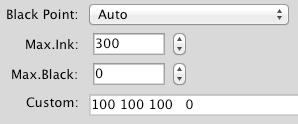
Ink limit: Allows limitation of the TAC for exported test charts. The upper ink limit is 100% per channel, so the TAC depends on the number of channels in the data, e.g. 7 channels result in a TAC limit of 700%. By default, the value is set to 400%, but higher values can be enabled after clicking the Lock icon. In general, the limit can be set as high as the channels allow or as low as 100%. ColorAnt uses a sophisticated ink limiting algorithm that does not just clip values.
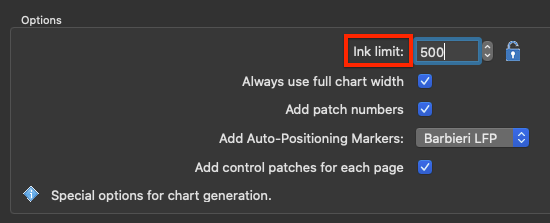
Note: Use the exported reference file for measuring and profiling so that reference values and test charts fit each other. Please note that the reference file will be ink limited, otherwise profiling would be leading to incorrect ICC profiles. Note that other profiling solutions may not be able to cope with a reference file that is reduced in the TAC. In addition, when building the ICC profile either use the same or a lower ink limit (called Max.Ink in ColorLogic CoPrA) than defined in the test chart. In most cases a decrease in the ink limit is not necessary for test chart creation.
Always use full chart width: When creating one-page test charts, ColorAnt tries to preserve the layout of the rows and columns during export, which can lead to an under-utilization of the chart width. To prevent this, activate the checkbox Always use full chart width.
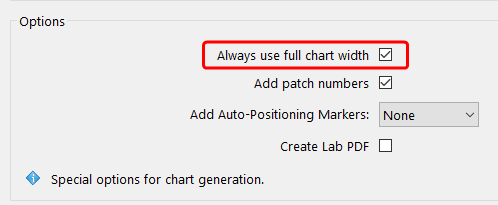
Note: Please consider the documentation of your measurement device. Some measurement devices allow measurement rows of patches by swiping over the rows. Those types of devices use rulers that can measure up to a certain width which needs to be taken into consideration when the Chart width is defined. The instrument documentation will tell you if a patch delimiter is required and will inform you about the minimum patch size.
Add patch numbers: Enabled by default. Disabling the option removes the numbers from patches.
Add Auto-Positioning Markers: To use the Barbieri or X-Rite auto positioning feature (Barbieri Spectro LFP and Spectro LFP qb, or X-Rite iSis), the chart needs the corresponding margins and markings. Select your device from the drop-down menu to add the required black auto positioning lines to every page of the test chart.
Note: Positioning markers printed in light colors can cause measurement issues. Charts that contain only light color channels and lack a dense or black channel cannot be measured with some measurement devices, like the X‑Rite iSIS or Barbieri LFP. This is because the data does not include a sufficiently dense or black channel to generate the required auto‑positioning markers.
Add control patches for each page: Adds control patches to check for stability if the test chart contains multiple pages. The patches are added to the top left on every page of the chart. Patches for 100%/70%/40% are added for each channel followed by a single white patch. This allows you to check for redundancies and production consistencies over different pages.
Create Lab PDF: If the checkbox is activated, the spot color library chart is exported as Lab PDF, whereby all spot colors are converted to Lab. In this case you can choose between PSD and PDF.
If the checkbox is not activated, the spot color library chart is exported as PDF, whereby all of the spot colors and their names are retained. In this case, a PDF file is created.
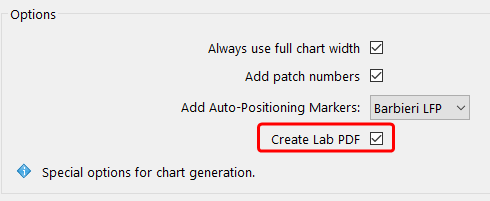
Important: By default, the checkbox is not enabled in order to retain the spot color names and channels.
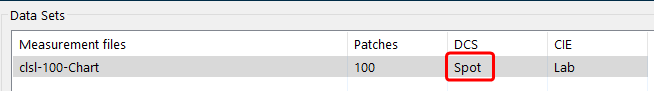
Note: The option is only available for spot color libraries that are defined as SPOT (DCS) or as NoSpace (DCS) in combination with Lab (CIE).
If a spot color library is not recognized as such, e.g., it is defined as CMYK, the datasets must first be unlinked using the Unlink DCS and PCS tool from the context menu (see screenshot).
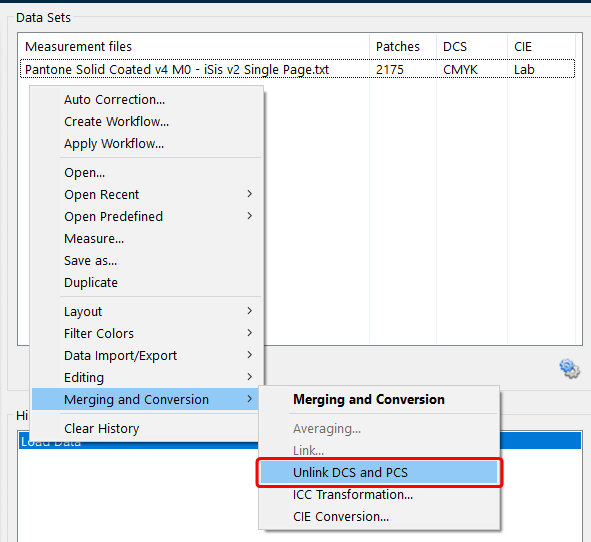
Unlink the data of the selected spot color library
This creates a file with NoSpace (DCS)/Lab (CIE). As a result, the Create Lab PDF checkbox becomes available in the Export Chart tool, and the spot color library chart can be exported as PDF or Lab PDF.
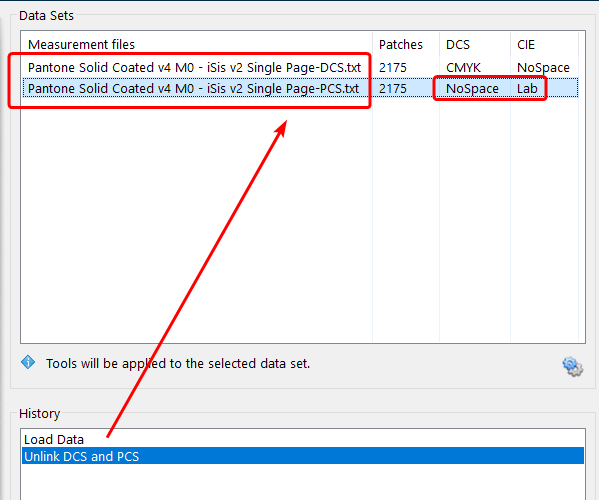
The resulting PCS.txt file is defined as NoSpace/Lab and can be exported as PDF