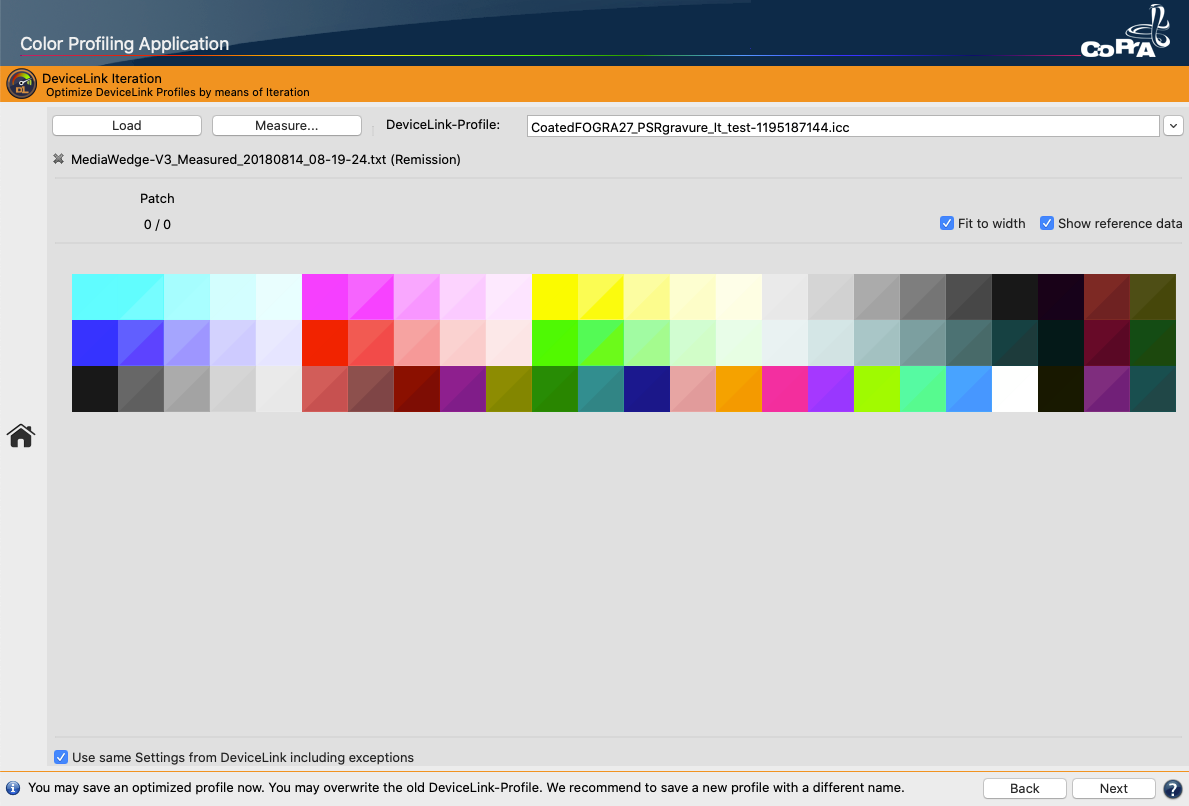
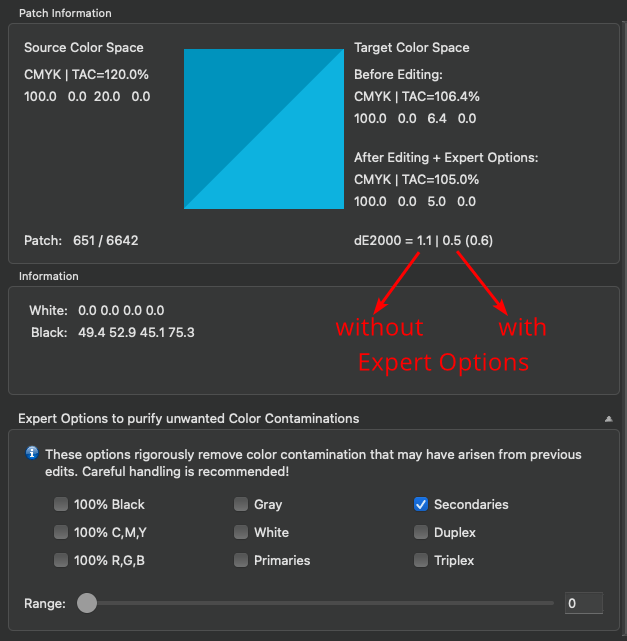
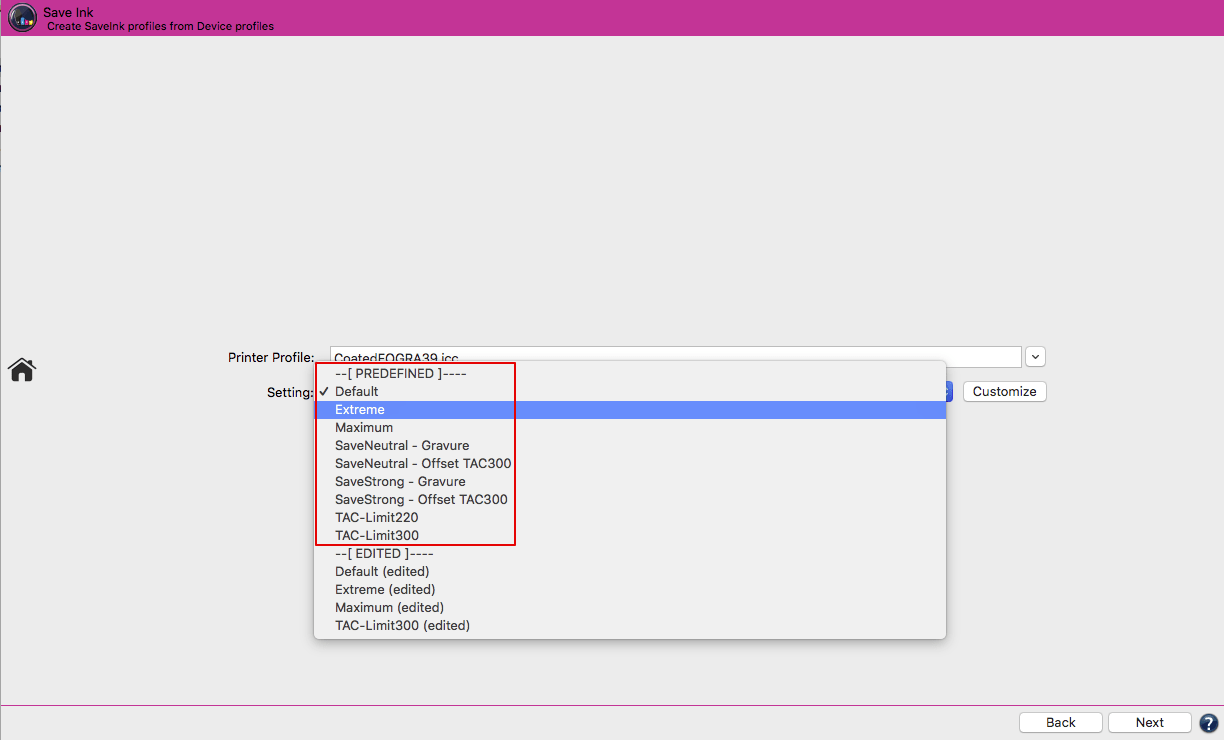
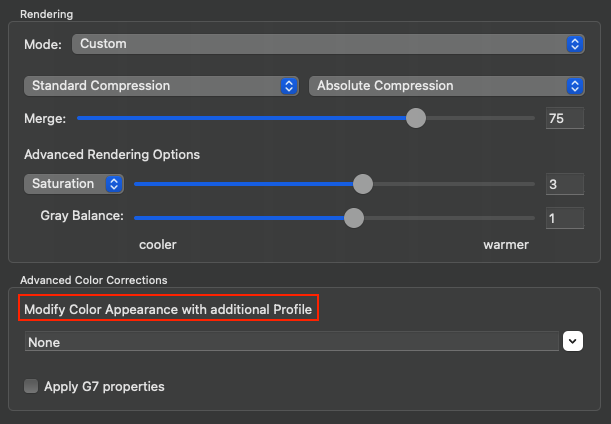
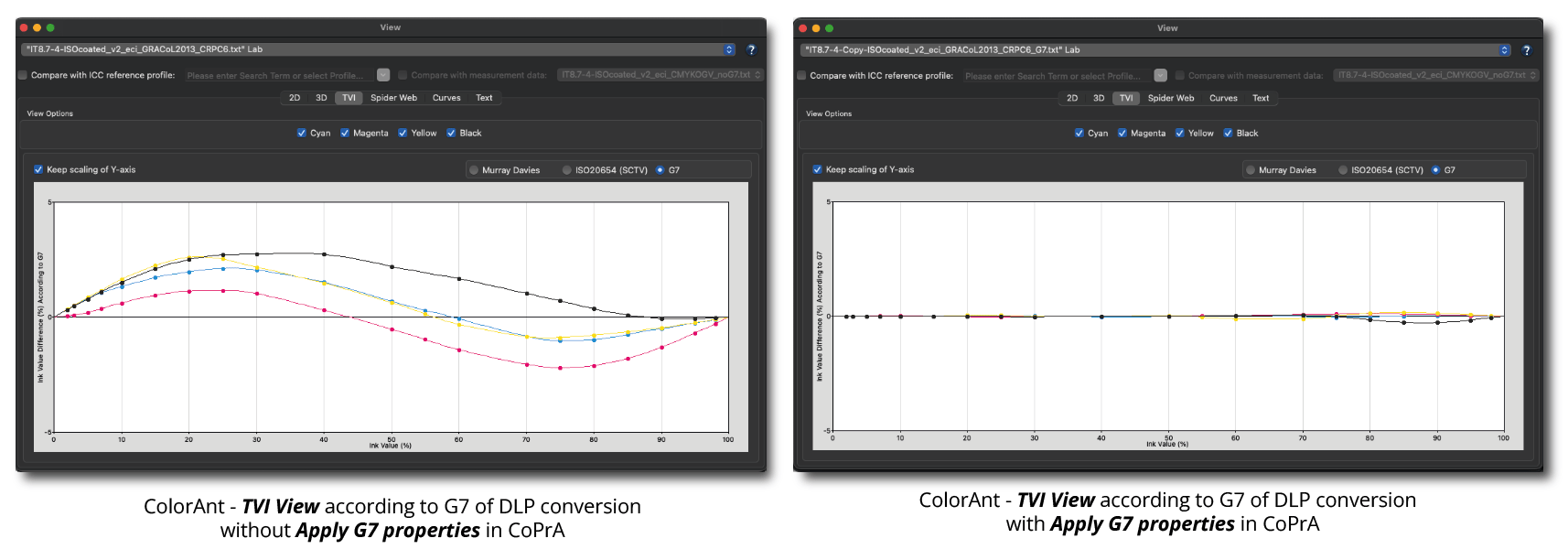
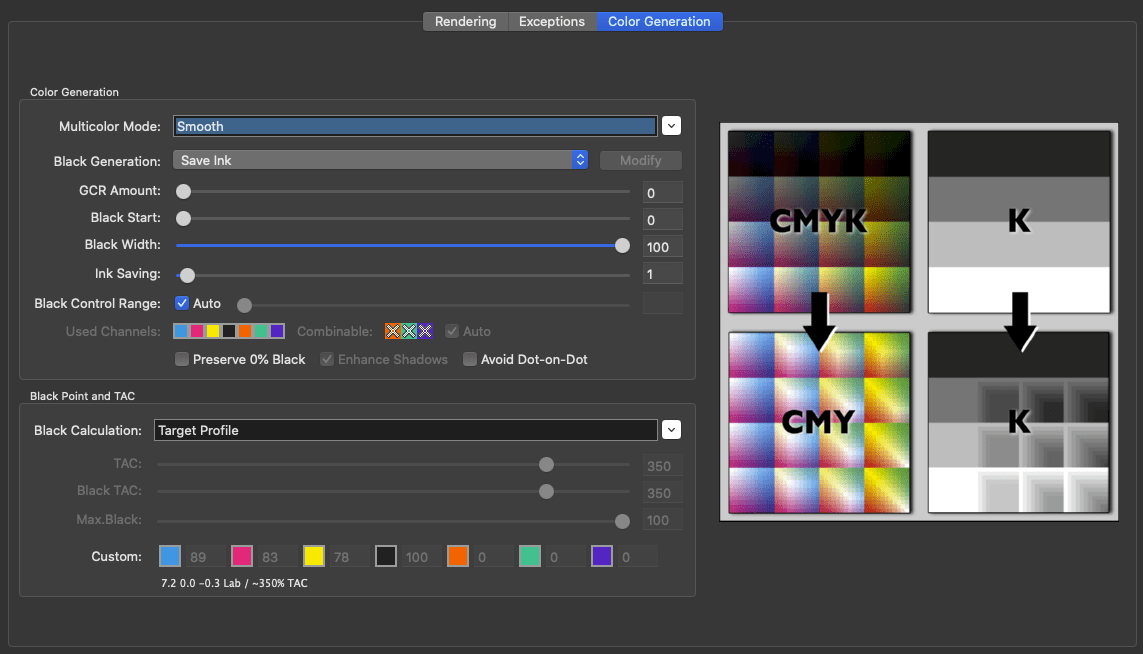
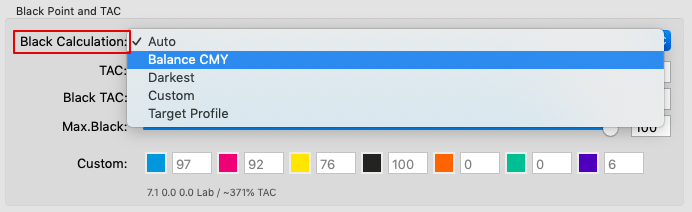
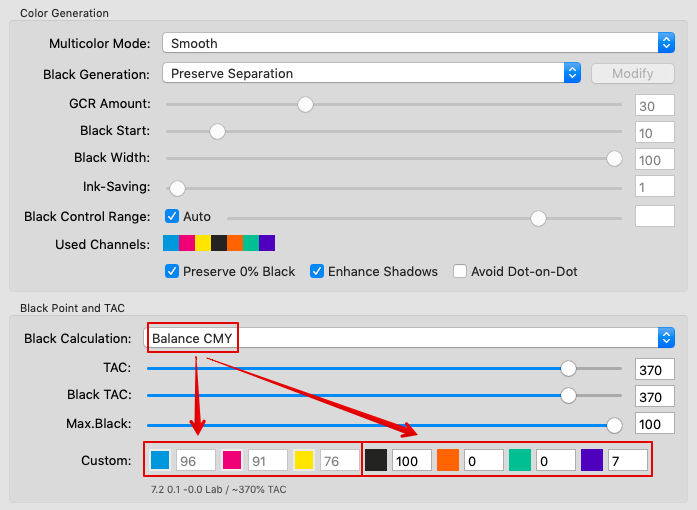
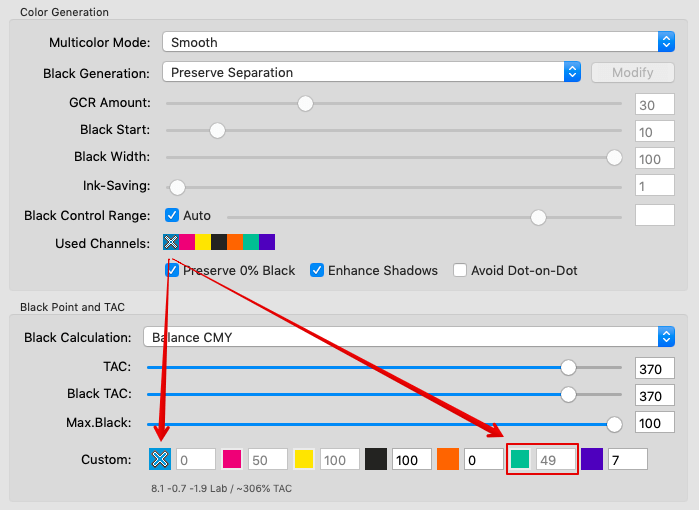
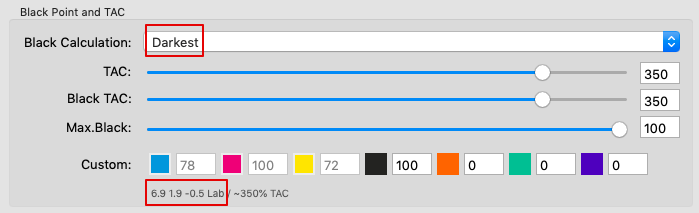
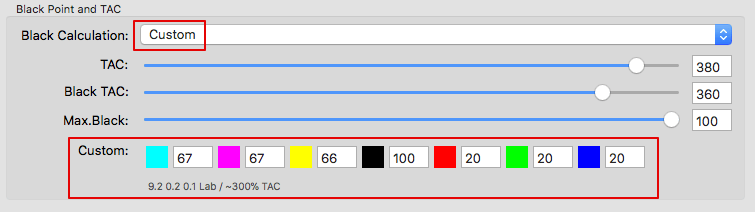
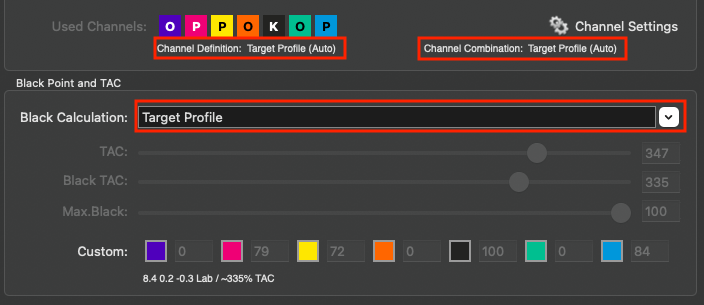
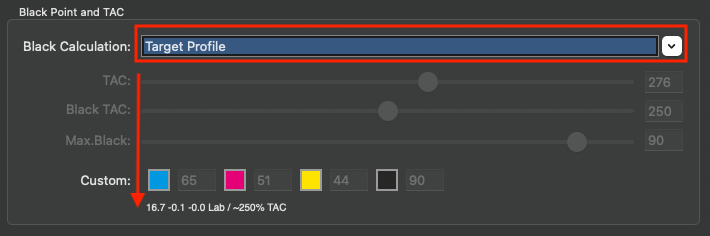
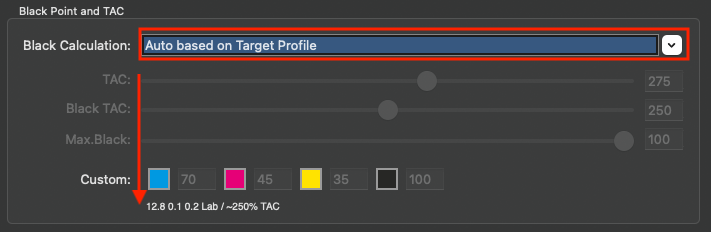
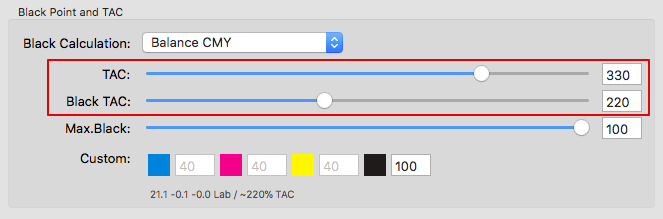
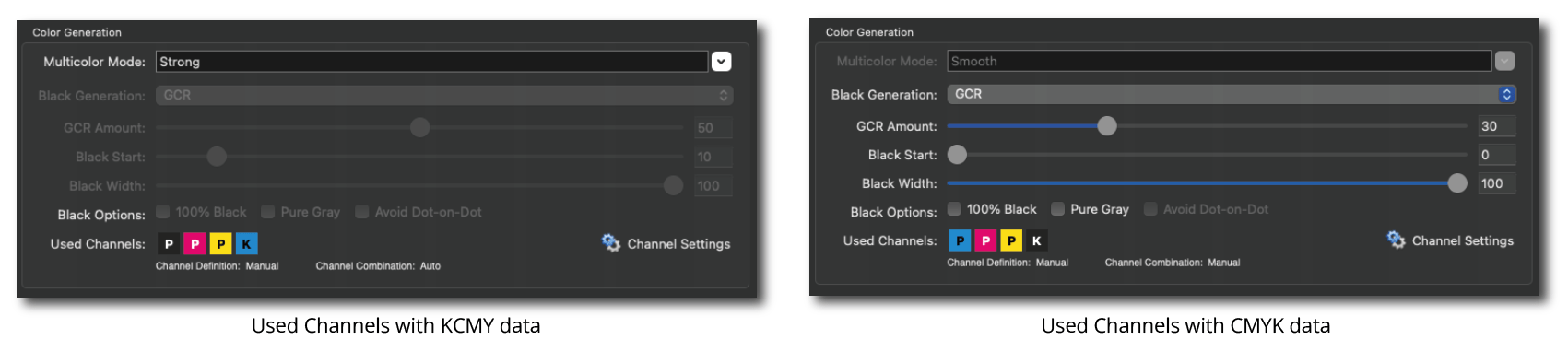
Defines the method for the generation of black in the target color space and therefore influences the separation comprehensively. Nine different black generation modes are available in the drop-down menu (depending on the licensed modules):
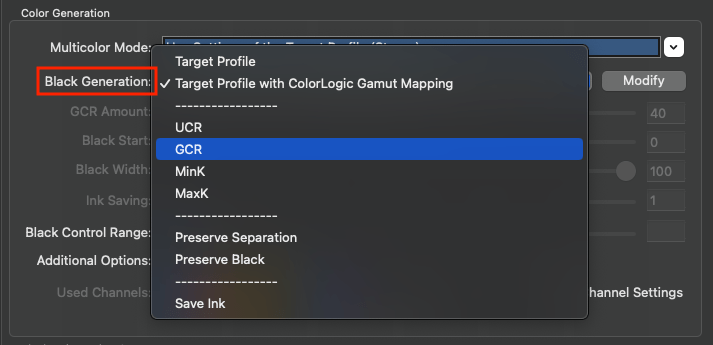
Target Profile: Uses the black separation and the out-of-gamut mapping of the target profile. Denies modifying the Color Generation and Black Point and TAC settings.
Target Profile with ColorLogic Gamut Mapping: Uses the black separation of the target profile – same as Target Profile – but recalculates the out-of-gamut mapping. Allows to change the Black Point and TAC settings. After clicking Modify the black generation settings can be changed as well. This way the settings of the target profile act as a starting point and can then be adapted to your needs.
Note: When clicking Modify the black generation switches to an appropriate mode closest to the target profiles settings (GCR, UCR, maxK…). This works best for ColorLogic printer profiles as the appropriate settings are exactly reproducible. For 3rd party profiles this may lead to a little update of the curves as with some profiles only settings as close as possible to those of the 3rd party profile will be found.
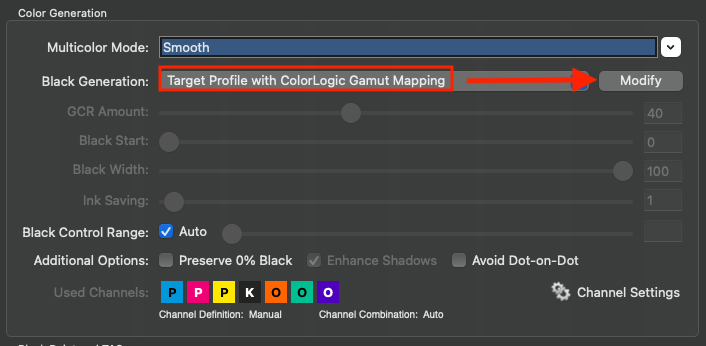
UCR: Allows adjustment of the settings Black Start and Black Width.
GCR: Additionally allows the adjustment of the setting GCR Amount.
MinK: Only uses a minimal amount of black and generates a separation using the maximum amount of CMY.
MaxK: Uses a maximal amount of black and generates a separation using the minimum amount of CMY. Is only available with a SaveInk license.
The methods UCR, GCR, MinK and MaxK generate a new separation, regardless of the separation of the target profile.
Preserve Separation: Preserves the ratio between the black channel and CMY composed black.
Note: The black generation mode Preserve Separation is especially important for conversions between similar CMYK printing processes (conversions between two offset presses or two inkjets of the same model etc.), because it ensures that the ratio between CMY and black which is used to generate gray is maintained in the color conversion.
When the mode Preserve Separation is selected, Enhance Shadows should always be enabled.
Preserve Black: Linearizes the black value of the source profile and retains the black channel.
Save Ink: Replaces CMY colors by black to save CMY inks. This setting is only available with a SaveInk license.
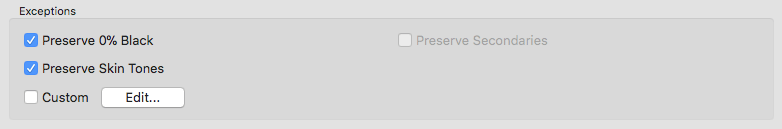
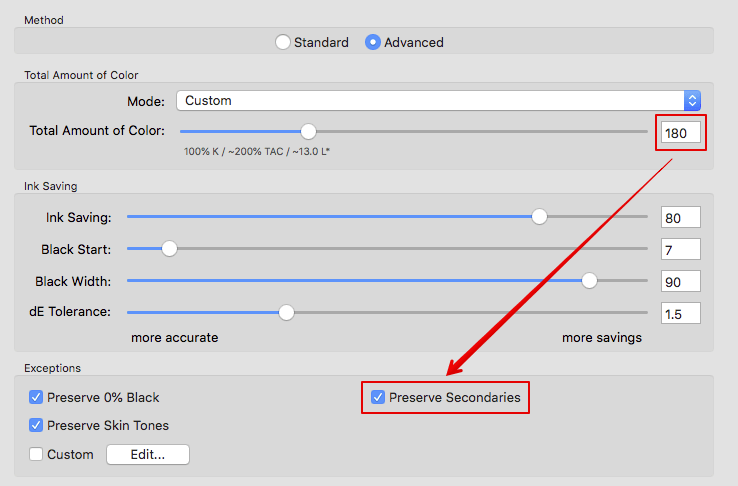
Preserve 0% Black: Is available when selecting one of the Black Generation modes Target Profile with ColorLogic Gamut Mapping, GCR, UCR, Preserve Separation or Save Ink. It prevents the generation of black in separations for source colors without black. This is important for some overprint applications.
Note: In order to use this function for the Preserve Separation mode, the Enhance Shadows checkbox must be enabled.
Enhance Shadows: Is also only available when the mode Preserve Separation has been selected. Prevents detail losses in dark colors and weak shadows.
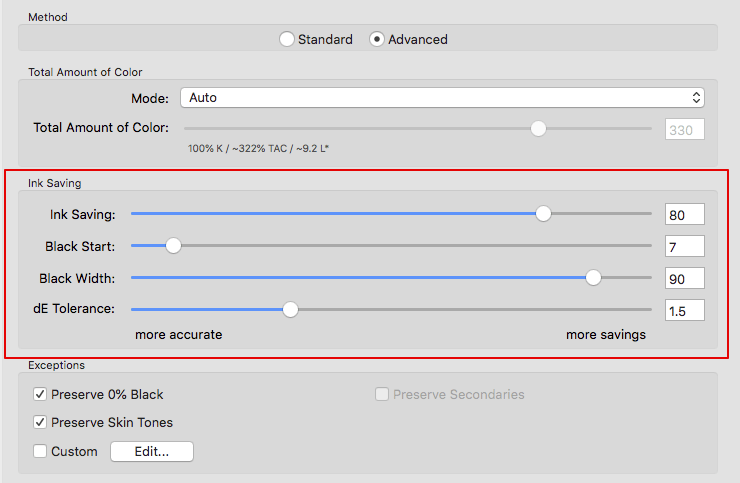
GCR Amount: Defines the amount of CMY that is replaced by black. At 0 only a low GCR amount is used which mainly impacts the shadows whereas at 100 a very strong GCR is used which affects the shadows and the highlights.
Black Start: Defines the starting point for the black generation. Black will be used if the minimum amount of C, M, Y exceeds this limit.
Black Width: Defines the range in which black is generated outside the color-neutral area. The lower the value the less black will be generated outside the color-neutral area.
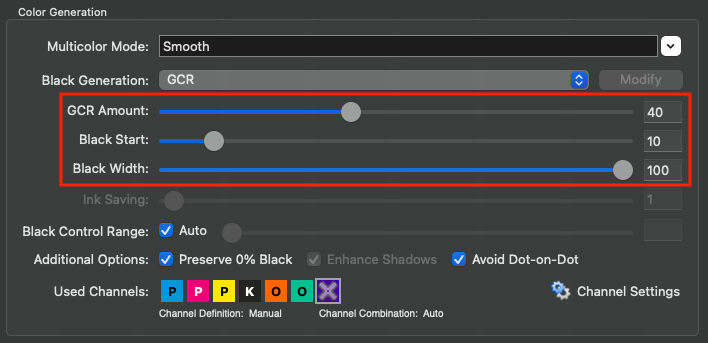
Ink-Saving: Replaces CMY colors by black to save CMY inks. This setting is only available with a SaveInk license (included in CoPrA XL and CoPrA XXL) and if the Save Ink option was selected under Black Generation.
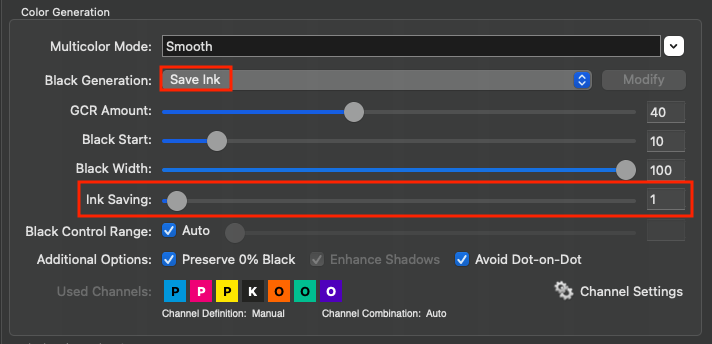
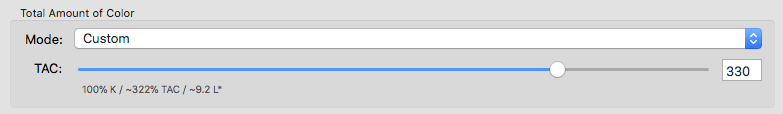
Black Control Range: Controls the transition to black. If black exceeds the limit, CMY colorants will not be modified and black is linearly added. Up to the specified value black will be calculated accurately. A value of 0% indicates that only CMY will be converted whereas black will be linearized. If a proof requires an exact colorimetric reproduction the slider should be set to 100%. 80% is a good value to achieve a smooth transition in the shadows. We recommend activating the checkbox Auto.
Additional Options
Preserve 0% Black: Is available when selecting one of the Black Generation modes Target Profile with ColorLogic Gamut Mapping, GCR, UCR, Preserve Separation or Save Ink. It prevents the generation of black in separations for source colors without black. This is important for some overprint applications.
Note: In order to use this function for the Preserve Separation mode, the Enhance Shadows checkbox must be enabled.
Enhance Shadows: Is also only available when the mode Preserve Separation has been selected. Prevents detail losses in dark colors and weak shadows.
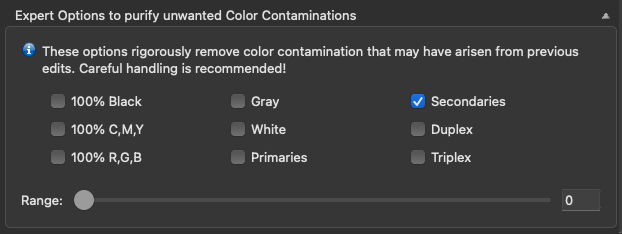
Avoid Dot-on-Dot: Prevents Black and Violet/Blue color combinations that could produce dot-on-dot effects in AM printing. Replaces some of the Black by CMY, therefore avoiding dot-on-dot effects.
Background: When using gamut extending process colors in traditional AM screening, such as CMYK+Orange+Green+Violet/Blue, the process colors Violet or Blue are often on the same screening angle as Black which can cause dot-on-dot issues leading to color and lightness variances. However, avoiding Black and Violet/Blue color combinations in separations would reduce the available gamut considerably and would also prevent dark bluish spot colors from being reproduced faithfully. By activating this feature the separation uses more of the CMY colors instead of Black thereby preventing dot-on-dot effects. For this function to work best, use a late Black Start and a rather weak GCR or even a UCR Black Generation setting.
Note: Other color combinations using the same AM screening angles such as Cyan and Orange or Magenta and Green are not affected by this feature as those combinations are rarely used in separations anyway.
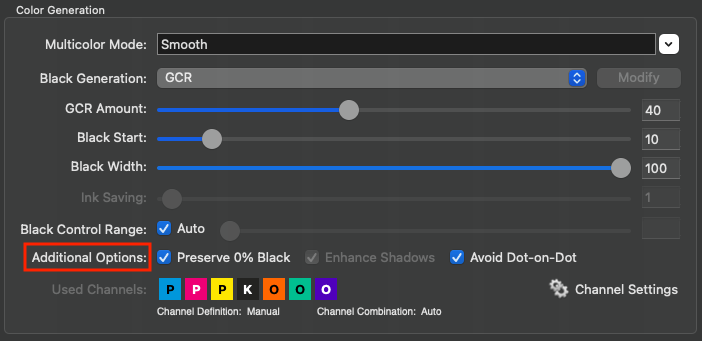
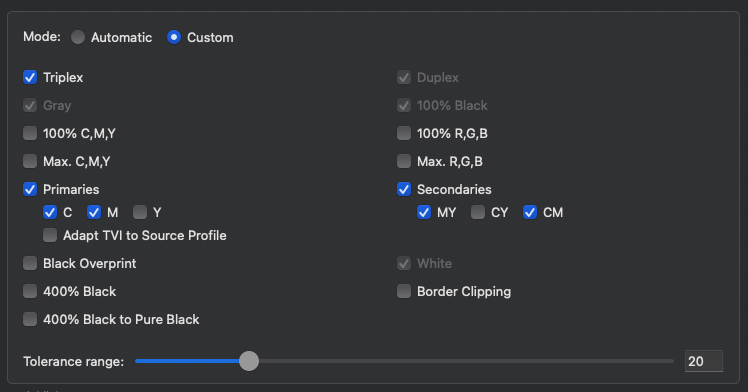
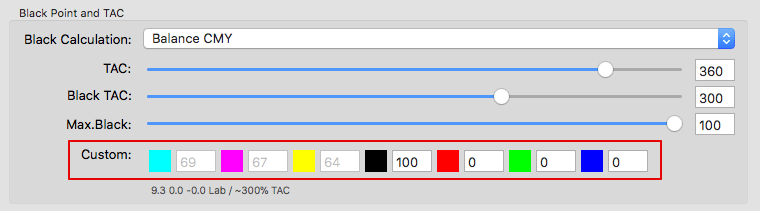
Used Channels: Displays the channels to be used in a profile. Excluded channels are grayed out and marked with an X. All settings that affect channels, such as channel definition, channel combination, or enabling/disabling channels, can be configured in the Channel Settings. This can be done both automatically and manually.
Note: If the Black Calculation is set to Target Profile, the black point is preset by the profile and the function Used Channels is deactivated.

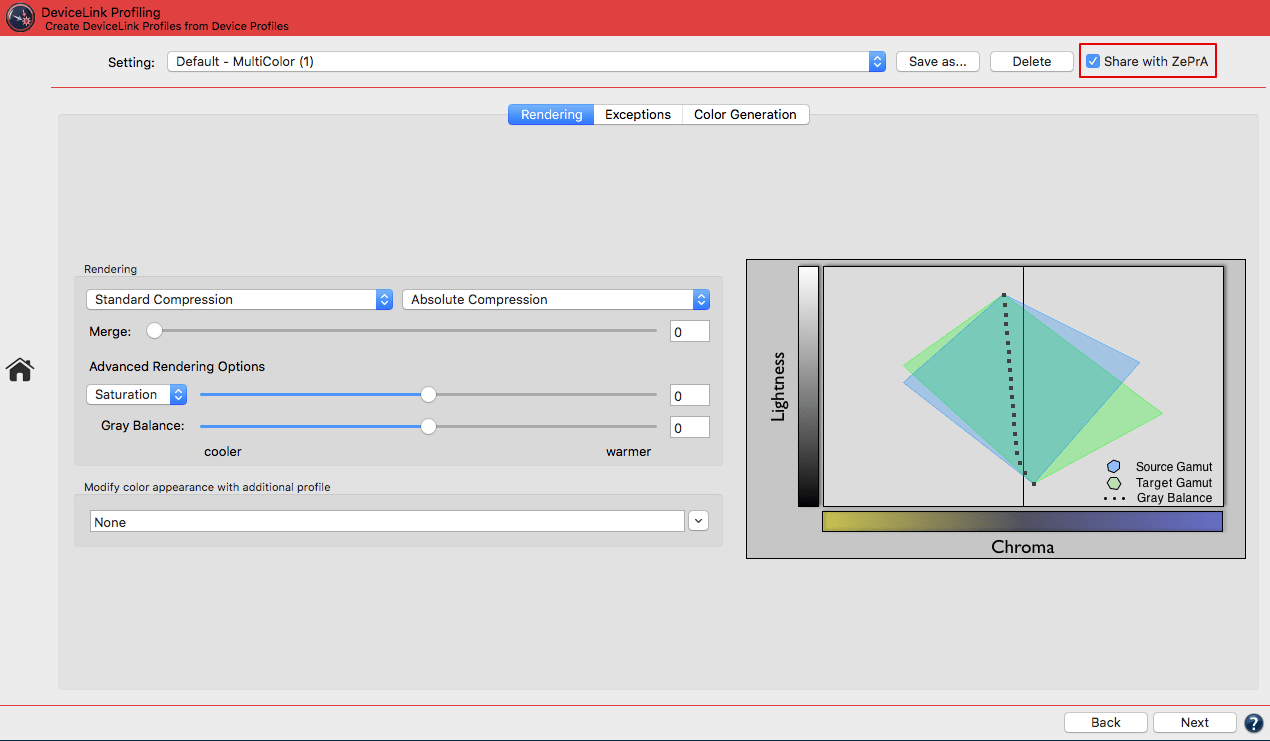
The effect of selecting or excluding colors on Curves and the Gamut is immediately visualized in the graphic and the Black Point value.
Note: The excluding channels function is particularly intelligent for Multicolor profiles, as it searches for replacement colors in the Multicolor channels when excluding a channel (e.g., Cyan), which can compensate for the missing channel in the gray balance. The alternatively calculated Multicolor channels are displayed grayed out in the panel Black Point and TAC (further information can be found in the toggle Black Point and TAC).
Example: If a brown chocolate artwork is intended to be printed in CMYK without using any Cyan in the separation, a CMYK printer profile can be created which only uses MYK. These types of profiles avoid unwanted Cyan dots in the separation and the converted artwork would appear visually close to a conversion with a complete CMYK profile. Obviously such a profile should not be used if the artwork contains Cyan based color combinations, such as cyan tones and blue or violet colors.
Channel Settings: By default, all channels of the profile are enabled, and all Channel Settings are set to Auto. Channels can be enabled or disabled by clicking on the icon of the desired channel. It is possible to exclude multiple channels.
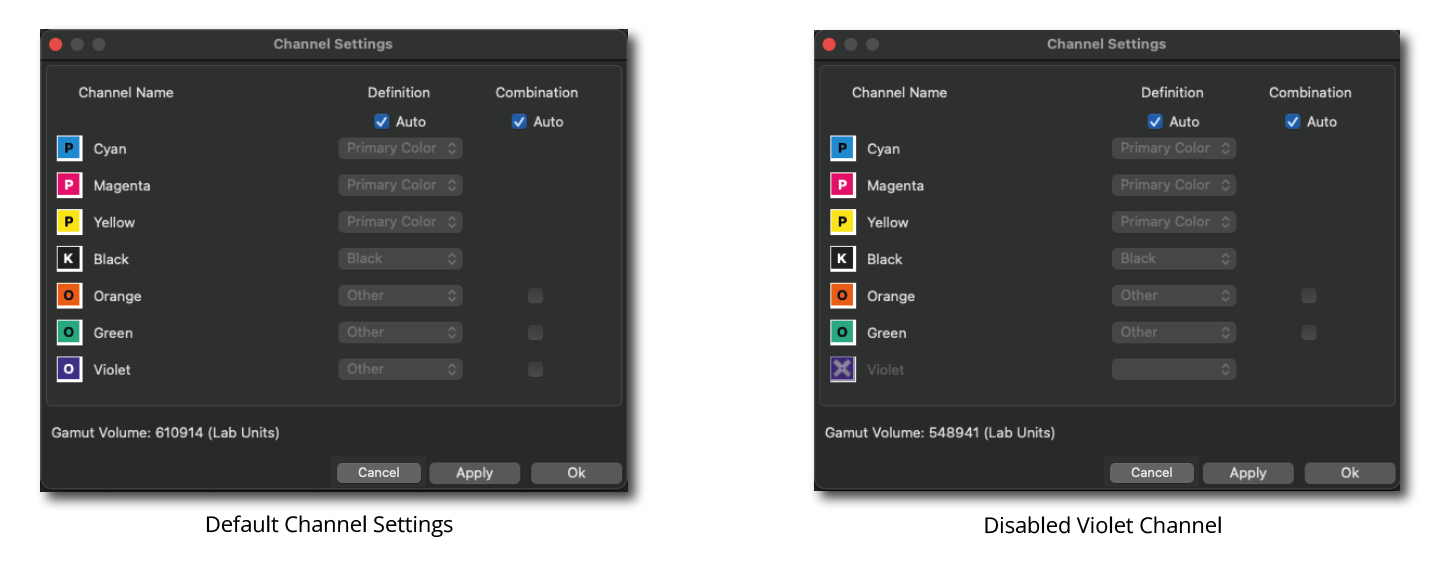
Note: In CoPrA, the default channel order in the measurement data has always been: Three primary colors (P), optional black (K) and optional additional (other) colors (O). This definition was applied regardless of whether the order could be handled correctly or not.
The Channel Settings option allows editing channels that are not defined in the correct order so that they can be used correctly in CoPrA.
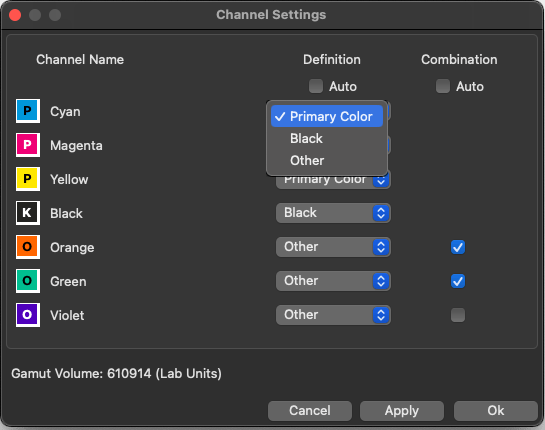
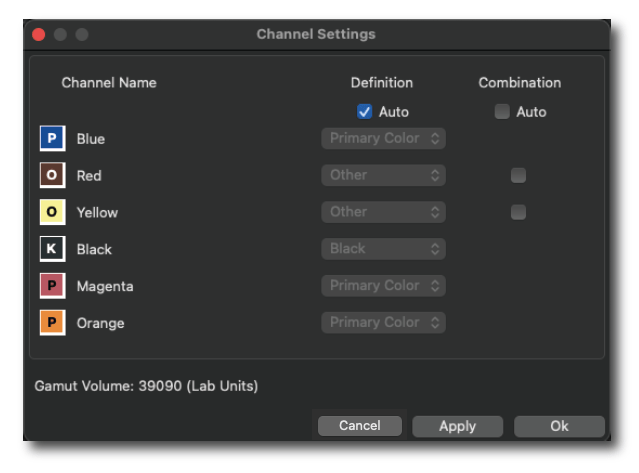
Definition: The channel Definition determines the assignment of the channels, i.e., whether it is a Primary Color (e.g., CMY), Black or another gamut-extending (spot) color (Other). This assignment can be done automatically or manually. By default, the order is set automatically (Auto).
An important element of the channel Definition is the inherent flexibility to achieve the maximum gamut volume from the measurement data used.
Note: There are several reasons why measurement data do not comply with the required printing sequence.
For example, in some applications, a specific color sequence must be adhered to on printing presses, and the RIP assigns a linearization to this sequence. The profiling chart is then defined and printed based on this sequence.
In other applications, such as ceramic printing, standardized CMYK colors are not used, and a specific sequence is not provided.
In addition, different densities of the colors used can result in colors being swapped to obtain a larger color space (e.g., Magenta and Red).
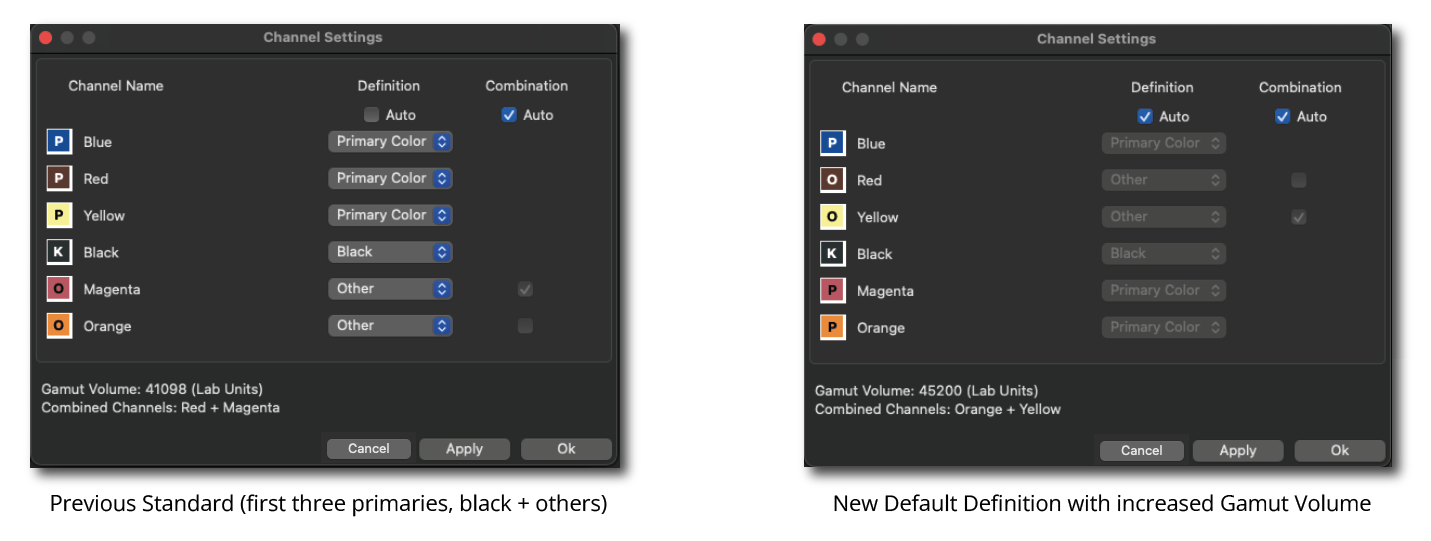
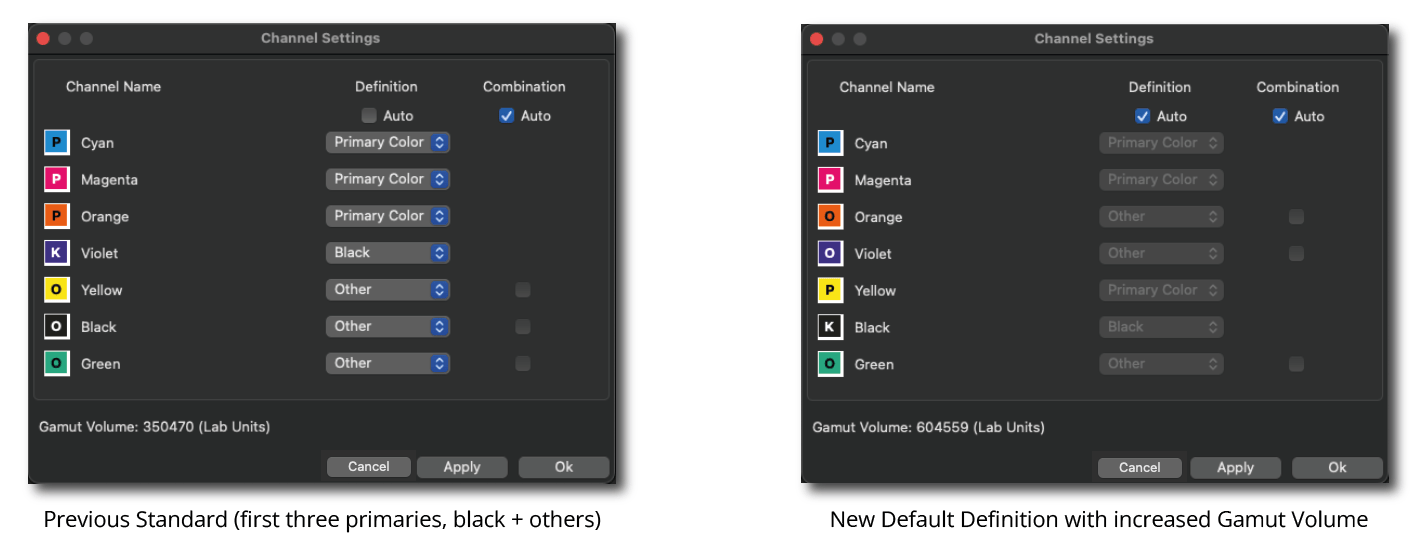
If Auto is enabled, CoPrA automatically calculates and selects the ink definitions and the combinations with the largest gamut. The size of the Gamut Volume and the combined channels are displayed.
Manual Definition: If required, the channels can be manually assigned a custom definition. There are three options per channel available.
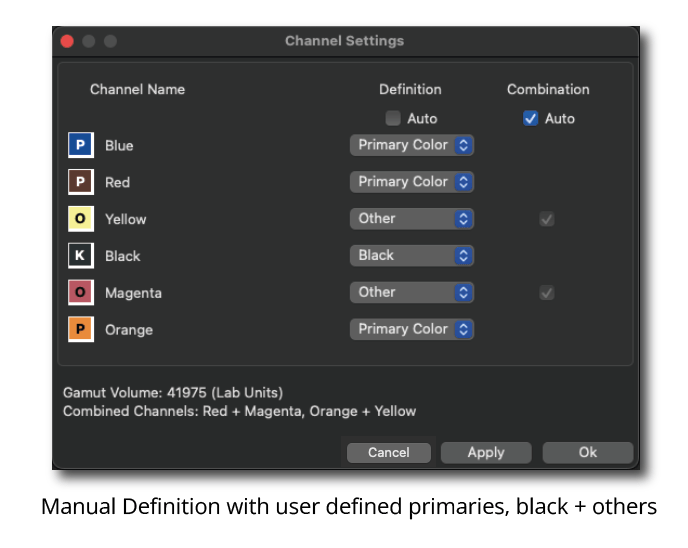
Primary: The data must contain three primary colors.
Black: One channel can be defined as black.
Other: Additional colors get the status Other.
After defining the channels and confirming the settings with Apply the Gamut Volume is calculated and displayed. By clicking OK the changes are applied and the window is closed.
Combination: The channel Combination specifies the Multicolor channels which are to be combined to expand the color gamut. This can be assigned automatically (which is the default for measurement data ≥4CLR) or manually.
Auto: This checkbox is enabled by default for all Multicolor presets. When enabled, CoPrA automatically calculates and selects the ink combinations with the largest gamut and indicates the combined channels. The combined channels are displayed in the Channel Settings window and also below the Curves and Gamut previews. In both previews CoPrA shows the impact of the combined colors by the Gamut Volume number.
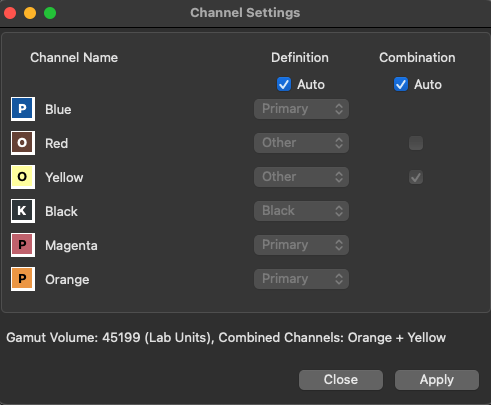
If the Auto checkbox is disabled, the channels can be defined manually by clicking the checkboxes of the desired combinable channels. If the additional inks are not to be combined with the four standard inks, the channels of the additional inks can be disabled.
Note: All profile settings, including those from the Channel Settings window, are embedded in the profile, and can be imported and used to reproduce settings by dragging an ICC profile onto the Setting drop-down menu. The name of imported profiles is given the suffix (imported).
Background: The channel Combination option is intended for creating Multicolor printer and DeviceLink profiles used in industrial applications such as ceramic printing, glass or metal decoration or textile printing, with Multicolor inks.
In these industries, special inks different from CMYK are often used in order to increase the color gamut in the shadows and some colorful areas, or to reduce costs.
For example, a dark Red ink can be combined with a Magenta ink of similar hue to extend the color gamut in the dark areas of the ceramic print. Similarly, a light Gray can be used in combination with the Black channel in Flexo printing to create a smoother gradient from light to dark grays.
CoPrA 8 and higher automatically detects if additional inks are either typical gamut-extending colors or special inks and will use them accordingly. For example, two inks with a similar hue but different chroma or lightness can be combined in a single channel.
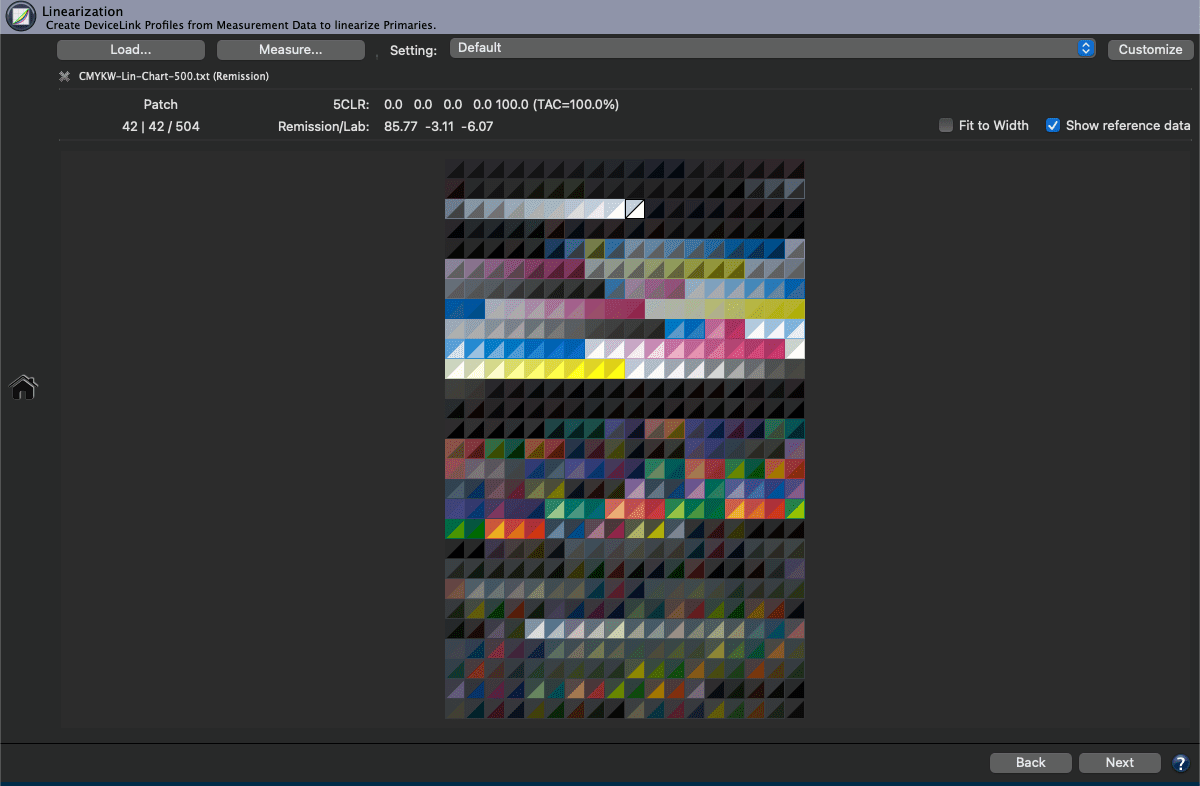
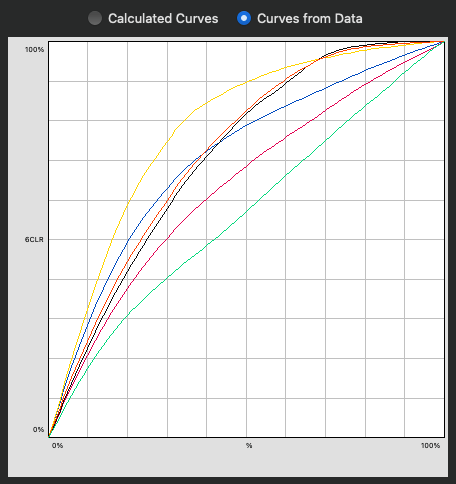
Example: If the Auto checkbox is activated, CoPrA calculates for the 6 color inks of the example data set (see screenshot) that the second channel (Magenta) can be combined with the 5th channel (a dark Red ink) to increase the gamut in the dark areas.
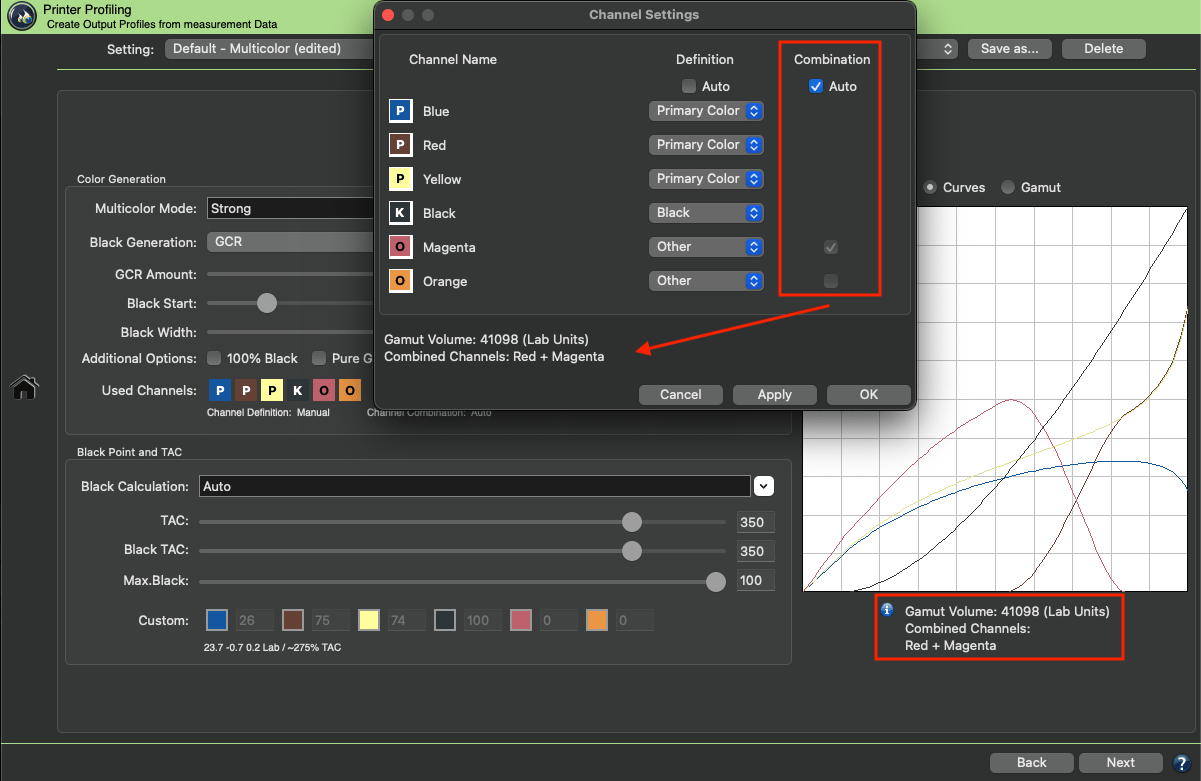
The Curves show that Magenta is used for lighter colors, while more of the dark Red channel is used for darker colors with the Magenta channel being reduced to a minimum.
On the other hand, the 6th channel (Orange) is a typical gamut-extending color and as such is automatically used by the selected Multicolor Mode in the Magenta-Yellow range of the color space.
The Auto function determines the best combination of additional inks and their combination with the 4 standard inks to achieve the largest color Gamut Volume.
Note: Typical gamut-extending colors used in ECG printing such as Orange, Green or Violet can not be combined with the 4 standard inks (CMYK).
In industrial printing, it may be necessary to use combinations other than those recommended by the Auto function. By deactivating the Auto checkbox you can select custom channel combinations, provided that a combination of inks is applicable.
Regarding the example in the screenshot, when the Auto checkbox is deactivated and channels can be combined, Magenta and dark Red are combined, and Yellow and Orange are combined, resulting in two channels under Combination.
If the dark Red channel is disabled under Combination, only the Yellow and Orange inks are combined. Switching to the Gamut view allows comparing the impact of the combinable channels on the Gamut Volume number.
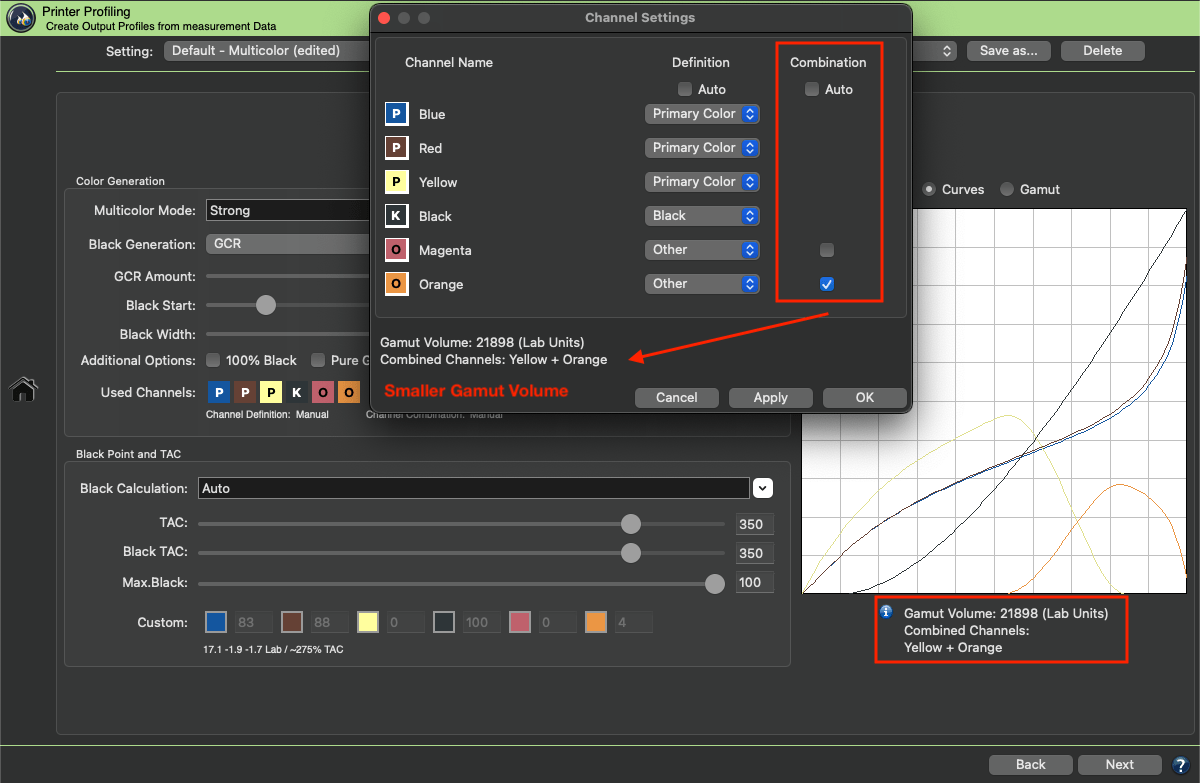
Note: The channel Combination differs from the Used Channels! Channels that are disabled under Used Channels are not used in the separation. Usually, it is recommended to use all channels and not to disable any channel if you want to combine channels.
It is recommended to use the default Auto setting for the channel Definition and Combination, as it automatically calculates and selects the ink definition and combinations with the largest gamut and indicates the combined channels.
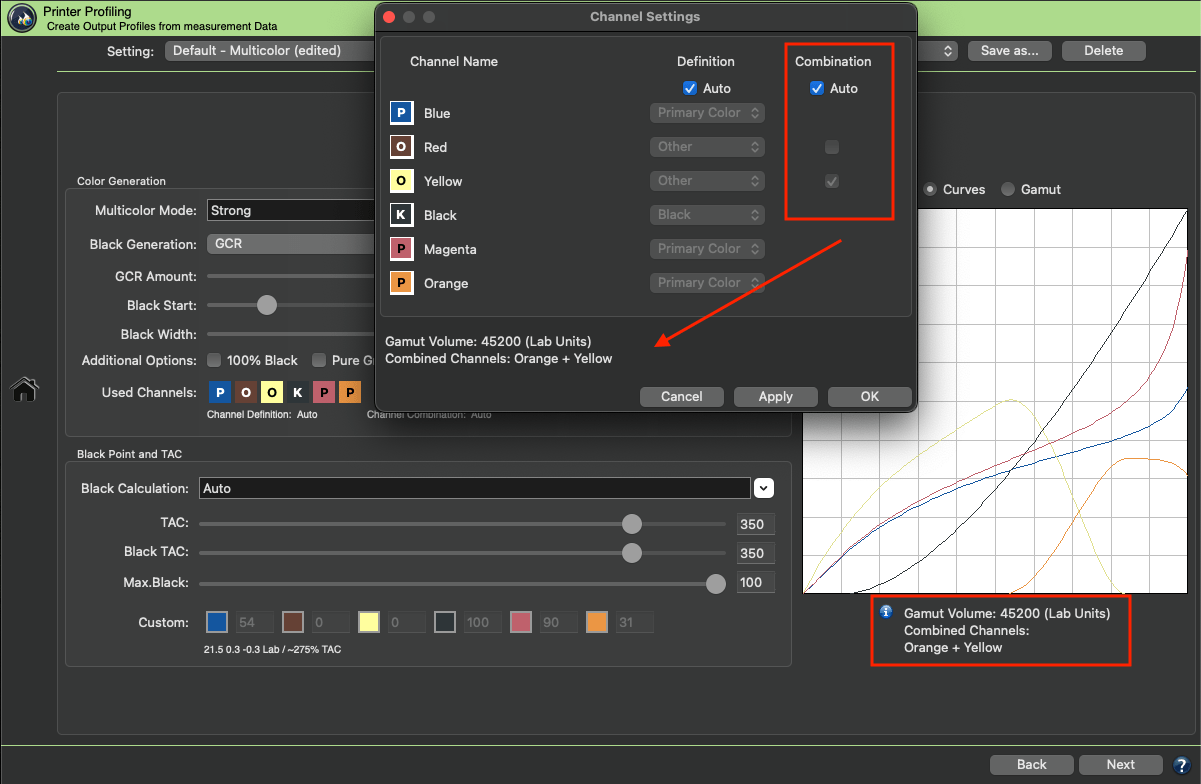
In our example the Magenta and Orange channel will be used as a Primary Color and Yellow is now combined with Orange.
Graphic: Visualizes the effects of the selected color separation and Black Point settings. Provides a real time preview of the loaded measurement data when altering settings.